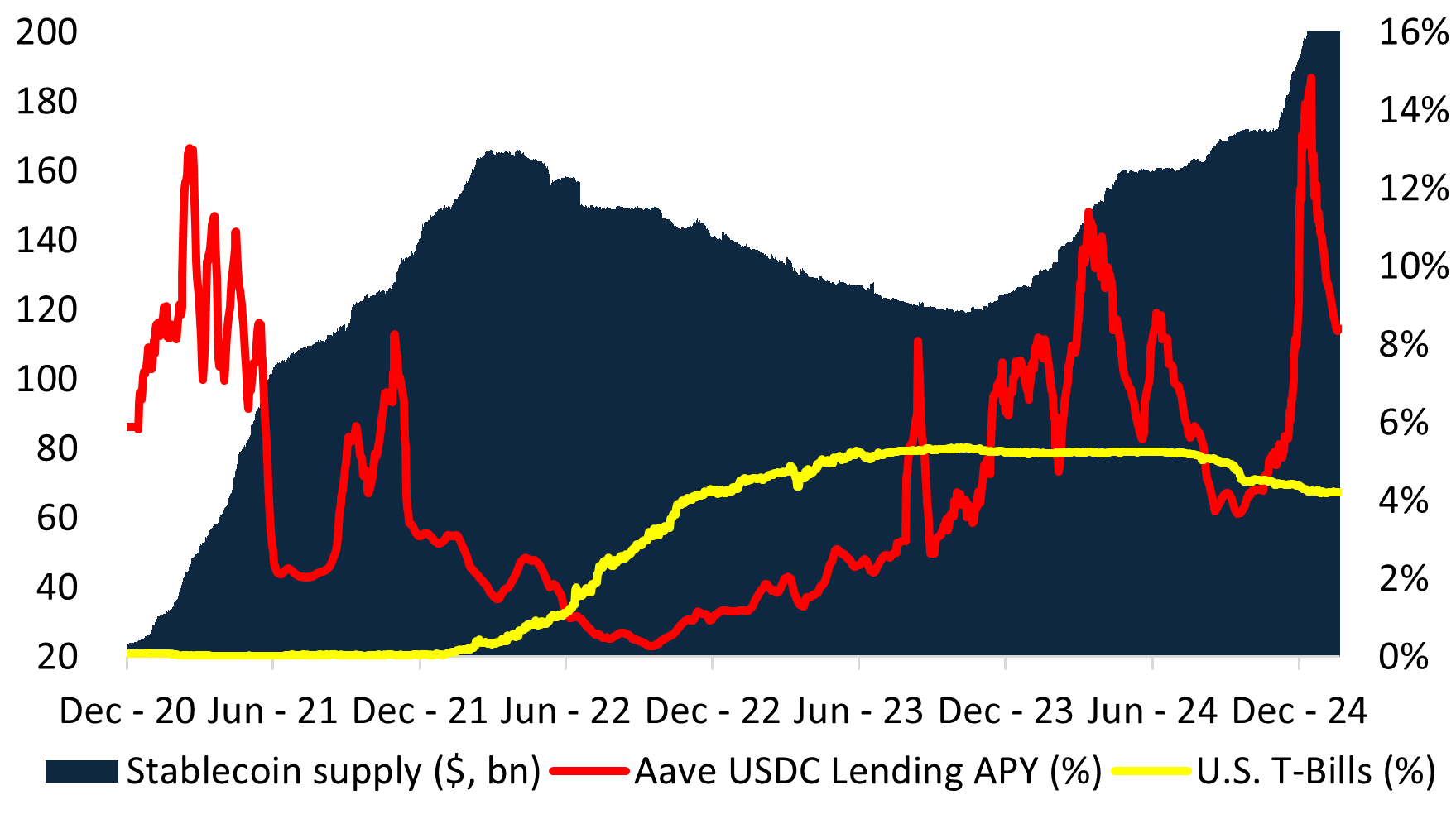
Більшість інтерв’ю стосувалися моєї нещодавньої історії, поточної дисертації та критеріїв відбору FJ Labs. Я був вражений, коли Гаррісон Фолл надіслав мені наступний список питань для підготовки до співбесіди.
Раннє життя та базовий досвід
1. Принстон
Питання: Ви вступили до Прінстона у 17 років, жонглюючи трьома роботами, експортуючи комп’ютерне обладнання до Європи, і все одно закінчили навчання найкращим у своєму класі з $50 тис. заощаджень у банку. Чи є якийсь особливий спогад з тих студентських років, маленька перемога чи тихий момент, коли ви зрозуміли, що ваші амбіції та наполеглива праця можуть відчинити двері, про які ви навіть не здогадувалися?
2. McKinsey
Питання: Після Принстона ви приєдналися до McKinsey і піднялися по кар’єрних сходах з рекордною швидкістю. Що дозволило Вам так швидко випередити своїх дуже здібних колег?
3. Окланд
Питання: Наприкінці 90-х ви адаптували модель eBay до Європи та Латинської Америки, залучили 18 мільйонів доларів – рекордну суму для французького стартапу. Що це була за компанія? Хто були ваші інвестори, і як виглядав ваш вихід з компанії?
Дослідницька записка: Залучила фінансування від Бернара Арно, який не хотів максимізувати свій вихід у грошовій формі. Пропустив придбання eBay за 300 млн євро через відсутність прав на купівлю, незважаючи на те, що володів 40% компанії. Зрештою, продали компанію, що котирується на біржі, яка обвалилася на 99%.
4. Засоби масової інформації
Питання: Французька преса була жорсткою щодо вас, коли ваш перший вихід на ринок не відбувся так, як ви сподівалися. Як ви пережили цей громадський резонанс, будучи молодим хлопцем, після того, як стали взірцем французького цифрового підприємця?
5. Zingy – повернення
Питання: Після розчарування в Aucland ви стали мудрішими і почали шукати конкретну бізнес-модель, яка не була б капіталомісткою. Зрештою, це привело вас до заснування Zingy, бізнесу з виробництва рингтонів для мобільних телефонів, яким ви не були захоплені, але все одно вирішили максимально використати кредитні картки, вижити на 2 долари на день у Нью-Йорку і були змушені кілька разів пропускати виплату зарплати. Що допомагало вам у найтемніші моменти, і що б ви порадили сьогоднішнім засновникам, які балансують на межі виживання?
6. Астрономічне зростання
Питання: Доходи Zingy злетіли з $1 млн у перший рік роботи до $5 млн, потім до $50 млн і, зрештою, до $200 млн! Вражаюча траєкторія зростання. Озираючись назад, що найчастіше ламалося на кожному етапі масштабування, і які рамки або способи мислення допомагали вам і команді швидко адаптуватися до цього постійного тиску?
Дослідницька примітка: Зіткнулися з величезними судовими позовами від звукозаписних компаній, довелося вирішувати складні юридичні питання та питання масштабування.
7. Продаж Zingy за $80 млн готівкою
Питання: Після запеклої конкурентної боротьби ви продали Zingy за $80 млн готівкою. Що ви відчували, коли не змогли зібрати жодної копійки, коли вийшли з компанії так успішно? І які уроки з того виходу ви винесли для себе, як ви думаєте про створення вартості підприємства та вибір часу для виходу з портфельних компаній сьогодні?
Дослідницька примітка: Залишався на посаді протягом 18 місяців, але мав інше бачення, ніж японські власники. Мав можливість придбати Shazam за $1 млн!?
OLX
8. Можливість
Питання: Після виходу з Zingy ви побачили, що Craigslist не був настільки хорошим, наскільки міг би бути. Розкажіть, будь ласка, про те, що ви побачили і як ви намагалися об’єднати зусилля з Craigslist, перш ніж створити власну значно покращену версію: OLX?
9. Глобальний запуск
Питання: Ви запустилися в 100 країнах одночасно, виділивши близько $50 тис. на кожен ринок для проведення експериментів і пошуку початкового зчеплення, зрештою зупинившись на Індії та Бразилії. Чи можете ви розповісти нам, як ви розробляли ці тести, і які ознаки підказали вам, на яких ринках слід подвоїти зусилля?
Дослідницька примітка: В результаті ми зосередилися на Індії та Бразилії, масове зростання, зумовлене SEO.
10. Масштабування OLX до 350 мільйонів користувачів
Питання: OLX виріс до 350 мільйонів унікальних відвідувачів щомісяця завдяки величезному успіху SEO та глобальній присутності в 50 країнах і 11 000 співробітників. Чи не могли б ви розповісти нам про один або два ваших найулюбленіших спогади про OLX?
11. Вихід OLX і конкурентна війна
Питання: В OLX ви були змушені боротися з європейським конкурентом, що призвело до дорогої медіа-війни. Чого ви навчилися, зіткнувшись віч-на-віч із закоренілими конкурентами, і як ви застосовуєте ці уроки, коли вирішуєте підтримати засновників, які можуть опинитися в подібному конкурентному середовищі?
FJ Labs: Критерії, процес та глобальне бачення
12. Питання: FJ Labs інвестує в близько 300 угод на рік, що охоплюють різні галузі та географічні регіони. Чи можете ви розповісти нам про основну тезу та стратегію, що лежать в основі цього масштабного, глобального підходу, і які типи ринків та бізнес-моделей ви вважаєте найбільш привабливими на даний момент?
13. Фантастичний послужний список FJ Labs
Питання: Маючи понад 300 виходів та 39% IRR, FJ Labs має чудовий послужний список. Чи не могли б ви поділитися нещодавньою історією успіху, яка найкраще ілюструє цінність, яку ви приносите стартапам, і те, як ви підтримуєте їх у ключових точках перегину?
14. Дев’ять запитань про маркетплейси, які ви ставите
Питання: У FJ Labs ви розробили набір з дев’яти критеріїв для оцінки маркетплейсів. Що це за критерії і на які з них засновники найчастіше не звертають уваги?
Дослідницька записка: Команда, бізнес-модель (економіка одиниці), умови угоди.
15. Поради MVP-маркетплейсу
Засновникам, які хочуть створити маркетплейс, ви б порадили використовувати типовий шаблон від wordpress для початку роботи? Як ви порадите їм дослідити цю можливість?
16. Рішення, прийняте на двох засіданнях
Питання: Ви бачите 300 угод на тиждень, але робите лише 300 інвестицій на рік, часто приймаючи рішення після двох годинних зустрічей. Що відбувається на цих зустрічах?
17. Глобальні та несподівані ринки
Питання: Ви підтримували такі різні ринки, як ринок гравію в Польщі та нафтохімії в Індії. Можете поділитися історією одного особливо несподіваного ринку, в який ви інвестували, що переконало вас піти на такий крок?
Дослідницька примітка: Надає перевагу фрагментованим ринкам, а не дистриб’юторам для інших.
18. Фандрейзинг та когортні показники
Питання: Ви так багато знаєте про важливість покращення показників когорти для стартапу в міру просування від посівної до Серії А. Якщо стартап бачить, що його нові когорти витрачають менше або купують рідше, ніж попередні, які стратегічні повороти або переоцінки ви б порадили йому розглянути, щоб уникнути занепаду?
Дослідницька примітка: попереджає, що якщо когорти не покращуються, то початковий ІЦП міг бути піковим.
19. ШІ та наступна еволюція маркетплейсів
Питання: Оскільки штучний інтелект продовжує змінювати галузі, як ви бачите розвиток ринків, що виходить за рамки простого пошуку продавця і покупця, і які нові тенденції або моделі на перетині технологій, попиту і пропозиції хвилюють вас у майбутньому?
20. Покращення портфоліо
Питання: Зважаючи на те, що у вас такий висококонцентрований портфель ринкових інвестицій, чи робите ви коли-небудь інвестиції на рівні “топ-ко”, які можуть бути використані у всьому вашому портфелі? Я думаю, що щось на кшталт Klarna чудово підійшло б для більшості ваших стартапів. Якщо так, чи не могли б ви поділитися з нами прикладами?
Особисті роздуми
21. Мінімалізм, сім’я та пригоди
Питання: Ви три роки володіли всіма предметами, окрім 50, що, на Вашу думку, є найціннішим у цій культурі показного споживання?
22. Найпам’ятніша пригода та покупка
Питання: Зважаючи на ваш життєвий досвід, яка ваша найкраща пригода і найкраща покупка, яку ви коли-небудь робили?
Презентація інтерв’ю від OpenVC
У цьому епізоді подкасту OpenVC до нас приєднується Фабріс Грінда, справжній піонер маркетплейсів, технологічного підприємництва та венчурного інвестування.
🎓 At 17, he joined Princeton, worked three jobs, and graduated top of his class
💰 Raised $18M in seed funding for his first startup—the largest seed round ever for a French company
📈 Built Zingy to $200M+ revenue, then sold it for $80M in cash
🌍 Founded OLX, a global classified ads giant with 350M+ users and valued at $3B
📊 Now co-founder of FJ Labs, one of the world’s most active angel investors with 300+ startup investments
In this episode, we dive into:
✅ The hard lessons he learned from his first major exit
✅ His framework for evaluating billion-dollar opportunities
✅ How he scaled OLX into a global marketplace leader
✅ His investment philosophy and approach at FJ Labs
✅ Advice for founders navigating hypergrowth & market expansion
The OpenVC Show is hosted by Harrison Faull, co-founder and managing director of OVC Ventures. OVC ventures is the sole investment arm of OpenVC, where 1,000+ new startups raise funds monthly.
Harrison’s LinkedIn: /harrisonfaull
Timestamps:
00:00 From Ambition to Action: The Startup Journey Begins
04:02 Building Auckland: The Rise of a Marketplace
06:27 Navigating Challenges: The Evolving Landscape of Tech
08:35 Lessons from Failure: Resilience in the Face of Setbacks
10:43 Reinventing Success: The Birth of Zingy
13:15 The Ringtone Revolution: A New Business Model
15:16 Scaling Up: Overcoming Initial Hurdles
17:27 The Art of the Deal: Selling Zingy
20:32 Life After the Sale: Reflections and Future Plans
25:26 The Journey of Hypergrowth and Selling a Business
26:40 Passion for Product Development
27:58 Identifying Market Opportunities with OLX
30:54 Rapid Expansion and Market Testing
33:40 Transitioning to Angel Investing and FJ Labs
36:01 FJ Labs: Investment Strategy and Criteria
43:46 Advice for Founders: Building Marketplaces
46:35 Navigating Growth Challenges in Marketplaces
49:48 Leveraging AI in Marketplaces
52:44 Closing Thoughts and Future Engagements
In addition to the above YouTube video, you can also listen to the podcast on Spotify.
Transcript
Fabrice Grinda (00:00.141)
play that role and little by little got a lot better but they promoted me and I’m like okay thank you bye time has come I learned what I need to learn and now the time has come to go and actually pursue my destiny and go build tech startups
Harrison Faull (00:13.515)
Amazing. OK, so you had that ambition to be a founder from a young age. You went out, you built your toolkit, you got your credibility working at McKinsey. Can you tell us a little bit more about your first startup, Auckland, or not your first, well, the first tech startup that you had after McKinsey?
Fabrice Grinda (00:27.667)
Well, first venture method, but prior ones were tech as well, but they’re just not big, right? Like they were more like, you know, I building computers, selling them with your classmates and friends. I built a BBS, like the ancestor of the internet. This is the first one that’s like venture backed, lots of employees, et cetera. So the issue is I graduated, I finished McKinsey, was 23. And the issue is I didn’t consider myself to be pretty creative. And you want to be in tech, but I didn’t know what to build.
And so I’m like, you know what, maybe to start, I’ll just take an idea from the US and bring it to the rest of the world. Also, a lot of the ideas, in a way, required a lot of, especially back in the day, where it was a lot more expensive to build startups, a lot of skill sets and or capital I didn’t have. If you want to build Amazon, you need billions in inventory and warehouses and supply chain management skills. If you want to build E-Trade, you need banking licenses, et cetera.
Harrison Faull (01:24.367)
Cloud didn’t exist, right? So you had to build the physical infrastructure, which was already cost prohibitive. Yes.
Fabrice Grinda (01:28.008)
yeah, no, I built my own data centers. I built my own data centers. We had to get Oracle database licenses, and Microsoft web servers. mean, just turning the lights on is like a million bucks. The times have changed. There were very few people that knew how to code. And you had to code for the web. And so even finding them, which is part of the reason I coded the full front end of the site myself, because I just couldn’t find anyone that I was happy with their coding.
So kind of randomly, I saw the site of eBay in June of 98. And it was another one of these aha moments of love at first click. I studied economics and mathematics at Princeton, including market design. And the idea of creating markets which have liquidity, which unlock a tremendous amount of value, resonated with me. And I realized, OK, if you go to these offline,
flea markets, you’re unlikely to find what you want. If you want to sell, you’re unlikely to find a buyer for what you have. But if you put all that online, you create this virtuous circle with ever more buyers, brands, ever more sellers, and so on and so forth. And I thought this is a something, yes, marketplace is of a unique problem of chicken and egg, but it’s a problem that I’m uniquely well positioned to solve, given that that’s exactly what I’ve studied. Market design, a measuring elasticity of supply and demand, to figure out what an effective take rate is.
Fabrice Grinda (02:53.597)
thinking through how you match supply and demand, et cetera. And so I decided to go and build an eBay for France and Europe, ultimately, which is called Auckland.
Harrison Faull (03:03.469)
Awesome. the journey with Auckland was off to a running start. I’m not sure how long it was before you had the largest fundraise of any French startup ever with $18 million and actually funded by the family office of Berno Arnard, I believe. Yeah. So you’re extremely young. You’re bringing this US model to Europe. You’ve had the biggest fundraise and you’re off to the races. The press are writing about you.
Harrison Faull (03:33.061)
You’re on the front page of several different magazines. Can you tell us a bit about the journey of building that company before we get into just as interesting the ending of that journey?
Fabrice Grinda (03:43.739)
Well, the beginning of the journey was interesting because in the US, there was a full-blown tech bubble going on. And it actually had not yet reached France. And so even though I built the company, I built the code we’d launched, it actually hadn’t reached the level of hype. And every VC I talked to, and I was like, I want to raise like $10 million, do proper fundraising. They were like, nah, it’s France, half a million or a million. And I just didn’t want to do that.
kind of engineered the press hype around the company and around me. People did not take PR very seriously. And so in France, the CEOs of the companies were like barely talking to the press. And I basically reach out to the journalists and say, hey, I’d like to tell you about what I’m doing. None of them would take me seriously because I was 23 or 24. But I’m like, you know what? I’ll come to your office and just chat. And of course, I had a compelling story to tell. So each
Fabrice Grinda (04:39.987)
One hour conversation led to an article. And then I became kind of the go-to person for them to ask questions about tech. So they would send me a question. I would send them the article back. And literally, they would copy and paste the article, publish it. I mean, they’re lazy. And so very rapidly became the go-to person to ask tech questions, first in the written press, then radio, and finally on TV, like the 8 o’clock news, et cetera. And at the same time, people started realizing this internet thing was bubbling.
Fabrice Grinda (05:09.996)
And it became a bit frothy and also like it switched from no one caring to everyone wanted to invest in the category and Arno amongst others started reaching out and saying, hey, we want to back you. actually, I remember he actually bid on a foosball table or his secretary did and like and the transaction went well and realized there was something there. and so talk to him and the other people. He offered the most the highest valuation and the most capital, which is why I chose
to raise capital from him. And we were off to the races, I used the capital, we launched a super successful TV ad campaign, which was a way to reach the masses then. Traffic exploded, we grew to like 100 plus employees in five countries, 10 million a month in GMV. Like things looked actually like we’d made the right choice and everything was going well.
Harrison Faull (05:57.052)
Yeah. Wow. Amazing. So you’re young, you’ve managed to convince extremely impressive people that this is the future. They’ve backed you, you’re off to the races, the model is working. Did buyers started appearing? I believe there was some talks with eBay at some point.
Fabrice Grinda (06:15.26)
So eBay, met Meg and Pierre early, before I raised the capital from Arnaud on Europe at Web. And they actually offered me like $25 million or maybe $20 million. And at that point, I owned 75 % of the company. But the delusions of grandeur and arrogance of a completely penniless 24-year-old at that point, I’m like, eh, whatever. It’s money. doesn’t mean anything. I’m doing this to build something meaningful.
Fabrice Grinda (06:43.027)
15 million is nothing. And I really meant it. And it’s funny because I literally, I didn’t even, yeah, I didn’t even consider it. Since then I’ve learned how hard it is to make money and how easy it is to lose it. But yeah, I was gonna make 15 million at 24 and I didn’t even for one minute consider it. I was like, nah, it’s nothing, I’ll make it later. But it doesn’t matter. And…
Harrison Faull (06:47.303)
just dismissed it, literally just managed to dismiss it out of hand like that. It’s similar to your heroes though, like Zuckerberg turning down a billion when he was building Facebook.
Fabrice Grinda (07:12.07)
Yeah. so, and for a long time, it actually looked like it made the right call, right? Like the company grew very rapidly and then eBay came back maybe nine months later and offered like 300 million in cash. So clearly the turning down 20 to take 300 despite the dilution that happened along the way made sense.
Harrison Faull (07:37.939)
And would that have been all cash? Would that have been part of the dot com bubble in terms of equity? And why ultimately did that?
Fabrice Grinda (07:44.979)
It was a cash offer, but frankly their stock is one of the few that held up during the dot com bubble burst because they were a profitable company that did very well. So either would have been fine, but actually it was a cash offer.
Harrison Faull (08:00.308)
Okay, so what’s telling, who’s stopping you taking 300 million nine months after the fund rate?
Fabrice Grinda (08:03.762)
Well, as a first-time founder, you make a lot of mistakes. One mistake is you shouldn’t necessarily raise the highest, the most money at the highest valuation. Picking a VC is like getting married. They need to be with you in good times and bad times. You need to see eye eye and where this is going and what the vision of the company is. turns out that when
the person backing you is one of the wealthiest people in the world, making more money is not necessarily their core objective. And I came to Arno and he’s like, no, I’m not a mere financial investor. Making 10X in six months, that’s not for me. I’m an industrialist. I want to be perceived as the old school guy who got the internet. And he’s like, no, I don’t want to sell. Normally I would not want to sell now. I don’t want to sell ever. I’m not in it for the money.
Fabrice Grinda (08:56.689)
And I was like, that would have been nice to mention when you invested in my company. And usually it’s not a big deal because today you have these standardized documents and you can, there’s a drag along if I want to sell, I can force other people to sell, et cetera. But again, when I signed these documents, I was 23, I had no idea what I was doing. I trusted my lawyer to negotiate the right things. Of course, they didn’t take me seriously. Even though they were very well known.
law firm, I don’t think they took me purely seriously because I was so young. And yeah, they did a really bad job, didn’t have any of the relevant rights to force a sale of transactions. So sadly, we grabbed defeat from the jaws of victory. And what would have been extraordinary, as I led to essentially nothing. Sold to a company that he wanted to sell to, whose stock probably fell 99.98 % from like $10 billion in market cap to
$30 million in 1999. I mean, it was a total disaster. basically left the company with barely less, more than I started with. But interesting life lesson at someone else’s expense.
Harrison Faull (10:06.057)
Yeah, mean a lot learned and not very much time. But in terms of dealing with that failure, that setback, I’m sure there had been several along the way, building such an explosive growth company, there’s always going to be problems every day, but nothing of the magnitude of seeing the value of your shares go down quite so drastically, coupled with you being the poster child of France’s tech guru. And I’ve read that the press weren’t too kind to you.
after that success became a bit of a failure in their eyes. How did you handle that? What kind of resilience? Did you have any tools, any techniques to help you get through that that would be helpful for founders to hear about today to manage that pressure?
Fabrice Grinda (10:49.437)
So first of all, I mean, look, I never took that seriously like, you’re worth a billion or whatever. first of all, I realize it’s monopoly money, right? Like, virtual value of your shares does not allow you to buy an apartment or car, let alone buy coffee. So it’s virtual. And I realize we’re in a bubble. And then at some point, the bubble would burst. So from that perspective, my feet were grounded on a
were reasonably well-grounded and didn’t let that success get in my head. The bigger concern for me was I had been at the right time, at the right place, the right skills, and I’d failed to capture that opportunity. I worried that this was a once in a lifetime opportunity where young people with the right type of skills and background were given an opportunity to in a way like shortcut the different path that you had to go through in life or hoops.
to become successful. And I’d blown the opportunity, even though I’d executed in many ways perfectly from a product perspective, getting liquidity, building a website, et cetera, from a financial perspective. But at the end of day, I didn’t do this for the money. So I’m like, you know what? Maybe the entry now is going to be this niche little toy thing that only nerds like me are going to play with. And there’s no money in it. But I like building something out of nothing. This is my form of creative expression. And so.
There’s no money in it, but I’d rather stay in the internet. This is what I love to do. And I’ll go and build it again. So yeah, I was bit disappointed and disappointing. But because I never led the hype game in my head, the disappointment was more about the fact that I’d missed the opportunity and now I was just going to be doing this little niche-y thing for the rest of my life. It wasn’t going be meaningful or big. So that was more the disappointment. But at the end of the day, I like, you know what? I like what I’m doing. That’s all that matters.
Harrison Faull (12:47.86)
Incredible resilience, but let’s not downplay the victories too much. Do you have a favorite memory of that time of building Auckland? Is there one particular moment where you felt, wow, I’ve achieved X or that was really special?
Fabrice Grinda (13:03.474)
The, look, lots of little victories, right? Like turning the lights on, having the first transaction, having, I mean, we created a TV ad that was so shocking that we won a silver lining con for like creativity to when I made the cover of the French Fortune basically, or being the eight o’clock, all these were amazing. There were two TV shows where they’re following me around in my life as a founder and like, and it was like,
Fabrice Grinda (13:32.178)
number one TV show in France. don’t know, like 20 million or 30 million people watching it. And an entire episode was just following me do business. It was pretty insane, the level of fame and recognition, et cetera, for a otherwise shy, introverted 25-year-old.
Harrison Faull (13:50.124)
Yeah, you must have been able to create this persona or been able to convince yourself that it was the right thing to do to get all this free publicity to advertise Auckland and also yourself. Was personal brand a part of this or were you always trying to push the platform?
Fabrice Grinda (14:02.48)
The, no, it’s both. Look, I thought it would be helpful for both getting traffic and getting revenues. I think it was more meaningful then than it is today. Like today, I don’t care for visibility. Like I don’t have a publicist. I don’t want a big following. I have exactly the right level of fame. I think it would get in the way if I was more well known in terms of my quality of life.
And so I don’t pursue it in any way, shape, form. It was a means to an ends. Ultimately, I don’t think it was actually all that as helpful as I thought it might have otherwise been. Perhaps the doing that in the early days probably helped me get fundraising or capital in a way that I wouldn’t have had otherwise. But it didn’t bring that many users. Because the users are not reading Forbes and Fortune and the Washington Journal.
Fabrice Grinda (14:57.939)
The two that were helpful were the big TV ones where they were following me around. But even then, it’s pretty short-lived. One big TV ad in prime time on one of the major channels would have probably had just as much impact. But I did like the attention. And I realized that speaking came very naturally to me. And I’m not sure I created persona. It was just myself. And I was like a.
Be your authentic self and I think it resonates when you’re your true authentic self to other people, even though, know, I’m probably not probably, I am more direct and transparent than most people and sometimes it makes people uncomfortable, people realize it’s genuine and that’s all that matters.
Harrison Faull (15:39.363)
Awesome. No, I think that’s great advice. And yeah, a persona might be good if someone’s too nervous to get out of the camera, but the best thing is being your authentic self. And it definitely comes across on camera if you’re able to tap into that. Okay. So we’ve had the massive rise, a lot of small wins and some big wins with Auckland, then the crash ultimately with the exit. And then you reinvented yourself to create Zingy for the audience that don’t know.
What was the business and why did you choose that particular sector?
Fabrice Grinda (16:14.714)
Zingy was a mobile media company, to be more specific, we basically sold ringtones in the US market. In the old school days of the Motorola flip phones and the Nokia phones, people loved to personalize their devices with wallpapers or play little games or ringtones, which were the bigger category. And I chose the category despite not thinking it was particularly a large value add for humanity, and I never even listened to music in my life.
Because my prime directives was I wanted to be a tech founder. And in 2001, when the bubble had burst and no capital was available, I needed a company that I could build with very little capital and make profitable quickly. And as I looked at the types of companies I could build, almost all of them required reasonably large amounts of capital that was essentially not available. And this one, the few companies that were around doing it in Europe and Asia, were all profitable. And I’m like, OK.
This is something that doesn’t seem all that hard to execute that I can go build. The US is like years behind. There’s no like text messaging within a carrier, let alone between carriers. There’s no mobile payment solutions. We’re like US dark ages when it comes to mobile. So let’s try to see if I can bring the mobile revolution to the US market. And so that was the genesis of the idea. Because I just want to be a founder and the idea didn’t matter. Now.
Ideally, of course, that wouldn’t have been what I would have done. Ideally, I would have built the company I wanted to build, but you need to deal with the constraints that are around in the environment you’re with. If there’s no capital available, build something that you can build in a shoestring that can be profitable, even if it’s not ideal. Use that as a means to an end to then go on to build the thing you want to build.
Harrison Faull (18:00.749)
Awesome. I like it. But can you give us an insight into the early days? Because I know you went on to have phenomenal growth and a fantastic exit, but there was a long period where cash flow wasn’t coming in. Sales weren’t happening as fast as you wanted them to because you were doing a B2B. You wanted a B2B model, but I think you got initial traction B2C.
Fabrice Grinda (18:22.01)
Well, the ideal model, the way it’s worked in the rest of the world was actually B2C. You sell directly to the consumer, but the consumer can pay through their cell phone and it works on every phone. In the US, you had all these different networks like GSM, TDMA, CDMA, IDEN, et cetera. They were all incompatible. None of the carriers had delivery mechanisms into their platforms that were open or frankly didn’t even have any of them. And there was no billing mechanism. So the only way to launch, frankly, as a proof of concept was directly to the consumer.
Fabrice Grinda (18:50.675)
where we literally hacked into the delivery mechanisms of the carriers to deliver. They didn’t even know you could do that. We hacked into it and showed we could deliver into the networks, and not all of them, a subset of them. And so in order to order the ringtones at first, you had to pick your carrier, pick your phone model only from one of the phones that were available, so you didn’t know what that was. And you had to enter a credit card number on the web. So you can imagine the volumes were extraordinarily low. And the music companies didn’t take this seriously.
Fabrice Grinda (19:20.4)
None of them wanted to give me a license. And in other countries like France, there is a centralized music repository where you can just go get a license and poof, you get a license to all songs and you pay whatever, 10 cents a download or 10 % of the revenues. In the US, there was no standard contract, no standard license, and even no database who owned what. So we had to go on this detective hunt of figuring out which artists worked with which.
Fabrice Grinda (19:50.259)
writers, songwriters, because we needed the mechanical rights which were owned by the songwriters, which were represented by which law firm to try to figure out by which music publishing company to try to get the rights. even when we did figure it out after a massive detective work, the music companies often didn’t want to give us the licenses. And so even though I was like offering to pay them, they just didn’t give us the time of day. So we did a number of different things. At first, I
Fabrice Grinda (20:19.57)
documented who owned what, we launched, violating every, we didn’t even have licenses, we violated every copyright law in the world, but we would actually be sending checks to the different music publishers as though we had a contract. And they pretty much all of them deposited it. And so eventually they caught onto it and the penalty was like $250,000 per download infringement, and same penalties. So I was starting getting sued for billions and billions of dollars.
Fabrice Grinda (20:48.337)
by all these different publishers. And the lawyer, so I get the season’s business letter or whatever and the billion, multi-billion dollar. And I would call the lawyer like, I’m so excited that you’ve reached out to me. I’ve been trying to talk to you for so long. This is amazing. And to be like, who is this crazy guy? I’m suing him for like a billion dollars and he’s like so happy to talk to me. And I’m like, look, I actually want to do the right thing. I’ve wanted to do deals. I’ve wanted to pay you. By the way, I’ve paid you. You’ve deposited the checks. You’re all the checks. So I would argue I have an implicit contract.
Fabrice Grinda (21:17.618)
And if you want to sue me out of existence, you can, but it’ll cost you more and then just settle with me. And so I ended up settling with all the music companies, obviously for what I owed them or maybe 2x what I owed them, not like the crazy penalties, and ended up being the only licensed player in the US. No one else was trying to, because they went after me and I was just friendly. And also I put every last penny I had in the company. I borrowed 100k on my credit card.
Fabrice Grinda (21:46.675)
We had no revenue, so I missed payroll, I think, 27 times. Every two weeks, we make payroll. If I missed payroll, I’d be like, I don’t understand. Something’s wrong with the bank. They suck. They keep not wiring. Of course, there’s nobody in the bank who had to wire. But then I’d meet someone and convince them to put 5K or 10K in the company to make payroll. And so that happened over and over again for the first two years, basically. But little by little, laid the groundwork for what would lead to the success, meaning
Fabrice Grinda (22:16.828)
got the licenses. Then in order to, I kept knocking on the doors of all the phone carriers, but they’re big, ginormous companies. They don’t work with startups. They’re afraid we’re not gonna be around in the future. And so I went to all the shows. They didn’t even want to give me a meeting. Like I would shake their hands, make sure they heard my name. And so to, I kind of engineered the first deal. I, MSN, just like the Microsoft portal, they were desperate for good revenues.
I paid them $100,000 to become their official ringtone provider with a tab ringtones on MSN portal. And then we got a press release, and that got a little bit of tension. Then got Motorola to inbound me, and they were like, hey, we’re running the ringtone portal by web for Nextel. Do you mind providing them to us? So that was our first contract. And then this friend came calling and says, hey, we’re thinking of launching ringtones. Do you have any license? And I gave them like 25 of them. And that took on. once that took on and worked,
Fabrice Grinda (23:14.45)
All the other carriers were like, wait, we need this. And it became a frenzy where we signed every operator in like a three month period. And there was a question of launching. We finally got that. we launched on Sprint in March or April of 2003. We didn’t even know how well we were doing because it was on their platform. We finally got the check August 15, 2003, which is when we became profitable. And so we were saved. I I lived on the
Fabrice Grinda (23:43.443)
couch at the office for two years like living at two dollars a day I could only eat ramen noodles. So I paid back my credit card debt, paid back the employees that had backed salary and then it became a rocket ship. We went from a million in revenues in 02, 5 in 03, 50 in 04, 200 in 05 and yeah this time we grabbed victory from the jaws of defeat.
Harrison Faull (24:05.572)
How much were people willing to pay for ringtones back then?
Fabrice Grinda (24:11.122)
More than you would think. I started 99 cents, then I increased to 149, then I increased to 199, then I increased to 249, then I finished at 299, and we never saw declines in volume. So 299 in ringtone. And if you were especially a teen, and you wanted really the latest hook of the latest song to provide social currency, and so people would change almost every week or every other week. So it became a much bigger business than people expected.
Fabrice Grinda (24:40.531)
And in fact, think I paid 50 cents, I don’t know, $5 or $10 million in one year when he had in the club and once paid similar amounts. mean, the top songs of the day were extraordinarily popular. And we were generating more revenue to the songwriters and the artists than traditional music sales, which at the time were being all pirated by Napster and whatever the.
all the different, lime wire and things like that.
Harrison Faull (25:08.199)
Let see. wow, what a journey, what a story. So astronomical growth, right? 1 million to 200 million in four years in revenue. And then you end up selling. It’s sold to a Japanese company, if I’m right on that. I have to say, like most people do, transition period, pass over your skills, make sure there are processes in place. And I actually found that process to be not as smooth as one would hope. Could you tell us a little bit about
Harrison Faull (25:41.98)
what you learned from selling and perhaps what you might not have known at the time, do you would like to advise other founders on now to avoid a similar situation?
Fabrice Grinda (25:50.579)
The first thing I learned in selling is use a banker. We were approached by the Japanese buyer in Q1-04, and they offered $40 million, which of course at that time I owned the majority of the company. It was like a life-changing amount. I was like, I’ve learned my lesson from the buy time. This is meaningful enough that I should probably take it. I hired Broadview, which now is called Jefferies, to run a process, and it doubled the price.
So we ended up closing with the same seller, but they ultimately bid $80 million. So I sold for $80 instead of $40. And by running process, making competitive, we increased the price dramatically. Number two, while you’re negotiating the stock purchase agreement with a buyer, having someone be the backup is very useful because you’re going to have to work for a certain period of time with a buyer. And so you can’t be the one creating a bad blood, negative relationship with.
Fabrice Grinda (26:45.235)
I would actually be the one driving the negotiations in the back end, like whatever I said, I wanted something different. would say, look, I love you guys. I wanna work with you, but my bankers are telling me this is on market and I don’t wanna look foolish. So, you know, if you change that, I’ll make sure it gets through. And so I appear as the good cop and the person solving their own. So bankers, amazing when it comes to deals above a certain price and definitely 40, 50 million pass that threshold. Number two,
Fabrice Grinda (27:14.066)
If you do an earn out, make it a revenue earn out more than EBITDA earn out because the buyer controls in a way your cost structure and so they can change your EBITDA and that will lead to that will lead inevitably to a loss. Much better actually if you have an earn out to be just time-based. You need to be there and making sure that easy things happen like the hand of control, a la la. Now in case, actually stayed longer than you might think. I stayed for 18 months.
Because actually in the early days it was fun. I was part of a hyper growth company going from 50 to 200 million. We were changing offices every six months. We were expanding the product lines, adding gaming, adding full-blown music ringtones, negotiating deals with labels. We even had the opportunity to buy Shazam for like a million dollars. Now, ultimately the reason I left is actually because all the ambitions I had, which included like buying Shazam, et cetera,
Fabrice Grinda (28:10.076)
were thwarted because the Japanese just said, no, I need the profits. And so they would take all my profits and ship it to Japan and didn’t let me continue building the empire. so we’re like, you know, at end of the day, didn’t particularly love the business, definitely didn’t like them. The cultural differences were large, but I don’t regret selling to them because they paid the most and in cash. And it was reasonably easy to keep doing my own thing on a go-forward basis. So I’m actually no regrets from that perspective.
I mean, I would have wished they’d let me continue to try to build it into something bigger by the fact that they didn’t lead me to the next adventure. So, regrets.
Harrison Faull (28:41.313)
Okay. So you’ve been living on $2 a day with ramen noodles four years ago. Suddenly you get this massive paycheck, all liquid, full cash. What’s top of the list? What do you splash out on straight away?
Fabrice Grinda (29:03.186)
Nothing, honestly, I stayed in the same studio apartment. bought a TV, an Xbox, and two tennis rackets, which probably cost me $1,500 max total. I didn’t do it for the money to begin with, and I saw money as a means to an end, like to have the freedom to build my next company without needing seed capital or pre-seed capital, to not have to worry about, like, you know, if I don’t…
Harrison Faull (29:11.243)
What?
Fabrice Grinda (29:33.219)
food again like the way I did for two years or rent or whatever but no there was I didn’t change anything into my life partly because we’re so busy or like like the more meaningful day was the day became profitable because the day we became profitable and I like that day full-on popped champagne like we were saved like we were the masters of our own destiny we were not going to die and and and that was like the probably to this day the most meaningful day of my like business career because like
Fabrice Grinda (30:03.026)
Until then, there was always a moment where it looked like we could die. And from that day on, was like, OK, now we’re saved. We’re good. Selling was just another step. But at the moment we sold, we closed in May or June of 2004, was the hypergrowth mode. Part of the reason I sold for, in a way, that little relative to what ended up being our 2004, 2005 revenues is in Q104, we closed 4 million revenues, 1 million EBITDA. And the Japanese asked me for my projections.
And of course, you never know these things. I’m like, yeah, I don’t know. We’ll make 20 million revenues this year, 4 million profits, maybe 50 million next year, 7 million profits. Had I known we’re going to do 50 and 200, I would have waited a bit longer. But again, better to leave it too late and better for cash and sock. But as a result, when I sold, we were growing like this. We were probably literally we’re moving off as I take an office, we were we were seven and we came.
25 for the time I moved office. Then I’ve taken office for 75 people. Like, yeah, we’ll never move out of that. Like six months later, like I was shit, we needed a bigger office. So we kept moving offices, hiring people, launching product lines, growing like crazy. I was working so hard that, yeah, it didn’t change anything in my life because my life was still building my business.
Harrison Faull (31:20.396)
Yeah, that’s amazing. I think it’s also extremely interesting that you found so much joy in the process, in the building, over the product. I’m sure you had to be a product expert or have someone there that loved it and made it perfect. But ultimately, you weren’t very aligned with the final consumer.
Fabrice Grinda (31:37.469)
So I didn’t love selling ringtones, but I actually like building product. And the nuance for me, the product is not that. The product is like the website, the user interface in the mobile apps of the different phones. And I love building product. I’m a product CEO. I’m the one writing the user stories. And these days, I’m like on Figma.
Fabrice Grinda (32:03.314)
like creating all the frames and then I use Canva to create different designs. So I love playing with products. I didn’t like the end product we were selling, but actually the product process of building the products. I love that. That I could do all day long. I I still do it to this day, right? I build my own AI, build my own blog because I love playing with products.
Harrison Faull (32:26.979)
I mean, it comes through. It’s energized and say, you’re passionate for it. And I’m sure it played dividends in your next step as well. moving forward to OLX.
Fabrice Grinda (32:38.247)
But actually, one comment, because when people are like, OK, does working really hard pay dividends? And the answer is absolutely yes. But if there two people competing, and one is doing it for fun, and the other one is doing it because they feel they have to do it, the person doing it for fun will win every day of the week, because it’s not work. It’s fun. And so in college, frankly, in high school, my first startup, yeah, I was working 100 hour weeks.
traditionally defined as work, but I didn’t think it was work, I thought it was play. And so, because I thought it was fun, I was just doing my hobby and being compensated for it. So other people that are doing it for work, they’re getting burned out. And if you do something you love doing, you don’t get burned out, it’s just what you do.
Harrison Faull (33:24.612)
I think that’s more true for founders because they encounter so many hurdles, so many no’s, so many failures. Unless you truly love it or you find some passion, some joy that makes you a little bit delirious and the 1 % that manages to get to the finish line, it’s extremely hard to get there without that. So there’s definitely a lot of truth to what you’re saying. So third company now, OLX which also went on to become an absolute juggernaut.
Harrison Faull (33:54.432)
For those of us that aren’t fully aware of that company, can you give us a bit of a market landscape and why there was actually an opportunity for OLX? Because I know there’s a really interesting story when it comes to Craigslist and what you tried to do there.
Fabrice Grinda (34:05.522)
Yeah, so 2005, yeah. So obviously my true love, originally it was marketplaces. So I kept an eye on what was going on in that world. And of course eBay had gone from strength to strength, 2004, 2005, Craigslist came into its own in the US and became part of the fabric of society. And it was a place to find roommates and apartments or jobs and items. And, but even back then it was already looked like it was 10 years out of date from a user interface perspective.
And just as importantly, I didn’t think they did a very good job in moderation. was full of scam and spam and phishing. They basically didn’t have a moderation team. The latest listings would be the latest posted. And then they would use the community to mark the bad ones to eliminate them. So all the latest listings were always the worst ones. It made no sense. So I went to see Craig and Jim. And I’m like, hey, I love what you guys are doing. You’re providing an amazing public service to humanity and the community. But we can do it better. Let’s moderate. Let’s improve the UX UI.
Fabrice Grinda (35:02.288)
You may not want to, you may not have the money for it, but how about that? I’ll do it for free. Like I just sold my company, I don’t need money. I don’t need anything. I don’t need equity, I don’t need cash. I will do this as a service to the community and to humanity. And no, they didn’t give me time a day, they didn’t care. They literally didn’t care. I think in one of the meetings they were like so high on like weed that they were like fading out of consciousness.
Fabrice Grinda (35:29.712)
And every time I met them since, they never remember meeting me before. was like pretty weird interactions. And I’m like, you know what? If I’m going to compete with someone, might as well compete with the person who doesn’t care. Now, the issue is in the US, they already had liquidity in marketplaces. Liquidity and network effects are so powerful that breaking them is very hard. But the opportunity was, while it was big in the US and there were few established incumbents in Europe, in most of the rest of the world, no one was doing this.
Fabrice Grinda (35:59.291)
And Classified is actually an amazing product for an emerging market because in countries where there’s no trust, where there’s no online payment, where there’s no shipping systems that work, actually meeting at your street corner and exchange a good for cash is actually a very viable option. And it’s like, know what? I’m going to build a better version of Craigslist for the rest of the world. We’re going to go mobile first. We’re going to focus on women because…
women are the primary decision makers in all household purchases, right? They decide the car you drive, the babysitter you hire, the house you live in, and pretty much everything else. And yet Craigslist is the least female friendly safe site in the world. And yeah, we’re going to start with consumer used goods because those are people buy them on a regular basis. So we get started getting a lot of organic traffic. And from there, we’re to go to cars and then real estate and then jobs.
Fabrice Grinda (36:54.836)
And yeah, that was the vision. I’ll pause here for now.
Harrison Faull (37:00.377)
Awesome. I mean, you didn’t go slowly. I read a little bit about your first go-to-market strategy, which seems bonkers, but there’s a lot of good thinking in there. Could you tell our audience a little bit of how you managed to launch in 100 countries to test the different markets? I don’t know over what period, but I imagine very quickly.
Fabrice Grinda (37:19.378)
Yeah, a couple of months. mean, basically, when you build a marketplace, you want to sort of supply, so you get sellers on the platform. And you just go to all the sellers, like car dealers, roles and brokers, like, look, I’m building a website. It’s free to list. I don’t have an audience right now, but perhaps you’ll get buyers. So do you want to list? And everyone kind of says yes. So you get supply. We built a little sales team in Buenos Aires in Argentina that was multilingual. That spoke all the different languages of the countries we attacked.
And we created the site, 100 countries, I don’t remember 30 or 40 languages, launched. And then we spent 50k per country, so $5 million total, to test where we could get the flywheel going of ever more sellers buying, bringing more buyers, and so on and so forth. And in these things, there’s a level of randomness. There are a few countries where it really, really resonated and really, really, really picked up in Portugal and Pakistan.
Fabrice Grinda (38:18.322)
And it picked up, lesser scale, but still very well for, I mean, bigger scale overall, but lesser scale is the market share of the country in Brazil and India. And so for the 100 countries, yeah.
Harrison Faull (38:27.368)
Sorry to interrupt, but what does that look like? What does that outlier look like? Is it 100 times return on your capital on the marketing? How obvious was it to spot here or was it marginal differences?
Fabrice Grinda (38:36.508)
No, it’s pretty obvious to spot because all of a sudden, every day, more listings, more buyers, more transactions, the flywheel just starts and just doesn’t stop. And even when you stop marketing, things keep going. And so it’s reasonably obvious. If we were listing an item, the probability that it would sell, at first, was 25%, which was already liquidity, but grew to 50%, 60%. So all the items listed would sell.
Harrison Faull (38:46.589)
wow, the flywheel had already started kicking in. Okay.
Fabrice Grinda (39:07.27)
consumers would be happy. And just like, yeah, it just kept going. So the unit economics were, by the way, underwater for a long time. So our revenue per user is like $1 or $2 a year at that point in time, because we’re only on an advertising model in countries with low GDP per capita. And acquiring customers would cost us more than that. Nonetheless, the idea that you pay for the first customers and then they lead to more
And so the flywheel, it was pretty obvious that the flywheel was working in these four countries. So we went from 100 countries down to four, really doubled down on the ones that we thought had real strategic value. Obviously, if we’re going to win Portugal back to China, might as well win it. But that’s not we’re going to create a multi-billionaire company. It’s going to be Brazil and India. So we really doubled down there, grew it, became very large, even profitable in Brazil. And then once we were there, used those profits to then rescale
Fabrice Grinda (40:01.053)
to 30 other countries and become the leaders in 30 countries overall.
Harrison Faull (40:05.961)
Okay, so you’re building another phenomenal marketplace, which ultimately gives you this incredible toolkit. You’ve been there, you’ve done it, you’ve had two incredible marketplace businesses, and you’re making some angel investments on the side. Did you start off by only wanting to angel invest into marketplaces, or did you have a bit of a spray and pray approach, but then ultimately found your footing with just marketplaces?
Fabrice Grinda (40:30.674)
So before I move on answering this question, I’ll give you a sense of scale. So OLX became huge, right? It’s like 300 million users a month. It’s like tens of millions of people making a living off the site every month. We grew it to, I think 11,000 employees at the beginning. Huge, huge company. Now, my vision mission was always be founder CEO. I never meant to be an angel investor. I never meant to be a VC. But what happened is when you’re a very visible internet founder, a lot of other founders come to you for advice and or money.
And so back in 98, at the very beginning of my journey, already other founders were saying, hey, can you invest in my startup? And so I thought long and hard, should I be an angel investor in parallel to being a founder? mean, it is a distraction in a way. And having thought long and hard, I ultimately articulated, I guess, three things. One is if I can articulate lessons learned to others, it means I’ve internalized them. Makes me a better founder. Number two, I’m running these horizontal multi-category sites,
eBay or Craigslist type sites. Actually meeting and keeping my fingers on the pulse of the market by meeting all the verticals and understanding the latest trends and business models also makes me a better founder. It’s actually useful to make sure I don’t miss any of the bigger trends. Number three, to minimize distractions as long as in a one hour meeting I decide if I’m going to invest or not and therefore I’m going to stick to things I know like marketplaces, it’s okay. So I created my four selection criteria.
Fabrice Grinda (41:58.035)
and started investing already in 98. And so by 2013, when I sold and left OLX I’d already made 173 investments, I’d like dozens of exits, even though was a secondary business for me. In fact, it was funny, in the US, I was known more as a super angel than I was known as a tech founder because OLX is not big in the US. So even though OLX is like literally one of the largest companies in the world from websites in the world, I was known as an angel.
Fabrice Grinda (42:26.74)
Even though that was like my night gig, not my main gig.
Harrison Faull (42:28.938)
Thanks. Amazing. Okay. So you saw it as an opportunity to actually help OLX, help yourself in that journey with marketplaces. You ended up formalizing that angel investing process by forming FJ Labs, which has gone on to make 1100 investments, 300 plus exits. It’s remarkable. It’s a VC fund, but a super angel type model. Could you tell us today what
FJ Labs looks like, what you’re looking for, what kind of investment sizes you do.
Fabrice Grinda (43:06.576)
Yeah, so first of all, we didn’t start out as a VC fund. We started really as my partner, Jose and I were like, hey, we like building companies, we like investing companies. It’ll be a family office to do that. And it kind of took a life of its own. we started getting, beyond getting it inbounded by massive volumes of deals, like every week we get 300 inbound deals, which required a structure. So we had to hire people, et cetera. We started getting inbounded by investors who said, hey, we want exposure where you’re doing.
can you let us invest? And that’s what led to our first formal venture fund in 2016 of like 50 million of external capital. It led to our second venture fund in 2018 with 175 million of capital from 20 LPs, third one in 21 with 290 million from 20 LPs. And we’re about to go to market. We’re going to raise fund four of 300 million in Q1 25. And we do fund every three years. So like fund five will be in Q1 28 and so on and so forth.
And so it kind of took a lot of it’s own, but to your point, we don’t behave like VCs, we behave like angels. You know, like two one hour meetings over the course of a week and we decide if we invest or not. Now, what are we looking for? I’ll answer it in multiple ways. You know, we, as I said, we behave like angel investors. So we invest in every category, in every geography, at every stage. But we’re 50 % US, 25 % Western Europe, 10 % Brazil, India, 15 % of the rest of the world.
We’re 70 % seed and A, so we’re mostly post-launch, post-revenue. We want to fund your growth, but we are also 20 % beyond words and 10 % pre-seed. We are 70 % marketplaces and network effect businesses, mostly in B2B marketplaces these days because you need to digitize the entire supply chains in the B2B world, which are at the very beginning of their digitization processes. And that’s everything.
moving the online ordering of inputs to online, or moving input ordering online, helping SMBs digitize, doing support infrastructure for all the payment networks, shipping, cetera. And I guess most importantly, what we look for is we have four selection criteria. So when we decide to invest in a startup, it’s four things. One, do we like the team? Now every VC in the world will tell you, I only invest in extraordinary founders.
Fabrice Grinda (45:27.398)
But it can’t be like porn. It can’t be something like, I only recognize it when I see it. And so for us, an extraordinary founder is someone who’s amazingly eloquent, visionary salesperson, and so Van Dijkers intersection of those two knows how to execute. And the way in a one hour meeting we evaluate if someone knows how to execute is number two selection criteria. Do we like the business? And for us, it’s like total addressable market size and more importantly, unit economics. Can you f-
recoup your fully loaded customer acquisition costs on a net contribution margin basis in six months? Can you three x in 18 months? Do you have negative revenue churn such that ultimately your LTV to CAC is like 10 to 1 or 20 to 1? And if you’re not there, why are you going to get there with scale without needing every star in the multiverse to align? And there are some VCs will say team is everything, the rest is relevant to them, but we care deeply about the business you’re in. Does it have a good economics? Number three, what are the deal terms?
Now, nothing’s cheap in tech, but is it fair? Is it fair in light of the traction, the opportunity, the category, and the team? And number four, what is the thesis? Is the thesis aligned with our vision of the future of the world? And we have clear visions for the future of mobility, of food, of real estate, et cetera. And we’re trying to solve three fundamental problems, so climate change and equality of opportunity and the mental and physical wellbeing crisis. Are you solving something we care about? And we want all four things to be true simultaneously.
So we need to love the team, love the business, find the deal terms fair, and like the thesis and the problem they’re trying to solve. And if all four are true, after two one hour meetings in a week, we’ll tell you we’re in. We’ll write the $400K check on average. And we’ll be super helpful to you in terms of fundraising and think through marketplace dynamics. But we won’t bother you. We won’t be on your board. We’ll take whatever reporting you’re willing to give us. And yeah, we want to talk to you really once a year when you go fundraise. And we’re going to make sure you nail your fundraising.
Harrison Faull (47:22.234)
Okay, wow. That’s quite a high benchmark. I imagine you have to see quite a few deals to build the portfolio size that you’re after here. Could you give us an insight on how much you actually see and what that actually results in over a 12-month investment period?
Fabrice Grinda (47:37.971)
So we see about 300 deals a week inbound. They come from three sources. We share a lot of deal flow with other VCs. So we’re friends with about 100 VCs. We talk to them once a quarter. So it’s about a VC a day per quarter. And we send them all of our best deals. And they send us in return their best deals. Now, of course, we’re more prolific than they are. So we send them more deals than they send us. But it’s kind win-win-win. When they send us a deal, we give them our perspective.
we’re going to help the founders with their marketplace dynamics, in return we send them a lot more deals and our founders get funded by the best VC, so they love it. And we’re not competing for allocation. They’re writing a $10 million check, we’re writing a $400K check, so it’s not a big deal. So these deals are probably the best quality. That’s about 100 deals a week. Another 100 deals a week are coming from the founders we backed before. 1100 companies, about 2000 founders, they come back from the next company. They send us their friends, they send us their employees. So of the deals we invested in about
Fabrice Grinda (48:33.747)
50 % come from the VCs, about 30 % come in from the founders. Now the last 100 a week come cold and bound, mostly through my LinkedIn, some direct to my email, but frankly Instagram, WhatsApp, I you name it, it’s like kind of all over. Mostly to me because I’m the kind of the vision or the face of the fund, even though we’re four partners, we’re 10 investors, we’re 35, so we’re pretty big. And it is still 15 % of the deals we do.
Yeah, a bit more, like 17%, but whatever. 15%, 20 % of the deals we do come from the cold inbound channel. And while they’re lower quality on average, some of the more interesting deals come from that channel because it’s like amazing founders. They just happen to not come from Sanford and live in SF. They’re in like Albany, New York, or they’re not in Sao Paulo, they’re in Palo Horizonte, and they didn’t go to the right schools. They don’t have connectivity. Of course, it’s better to get a warm inbound, but if we don’t have it, that’s fine too.
And so we see through any deals, we take calls about 50. The other 250 are often completely out of scope, biotech, hardware, et cetera. If there’s not a marketplace network effect type dynamic, we’ll do any industry, but it has to have that. So if you’re telling me you’re building a marketplace for something in space, that’s fine. But if you’re building rockets, we’re less likely to invest. And same thing in biotech, a marketplace for labor in biotech, no problem at all.
for buying or selling components, but if you’re just building a biotech company, not for us. A lot of Out of Scope, a lot is also just too early. Look, we do do pre-seed and pre-launch, but because we don’t invest in competitors, if eight people were pitching us the same idea at the same time, we want to wait until one of them emerge as the early leader before we pull the trigger, because if we’re wrong on the bet in pre-seed, then we’ve shot ourselves out of the category completely.
So we’re more likely to wait until C or A than do pre-seed unless you’re a second time founder or third time founder, and we’ve backed you before, then we’ll do pre-seed. But our pre-seed bar is very, very high. And so we take these 50 calls a week with a 10 % investment team. It’s a one-hour call. We evaluate the four things I discussed. We have a two-hour investment committee meeting on Tuesday, every Tuesday, from 10 to 12. We review the 50 deals. We take a second call with maybe 10 other companies.
Fabrice Grinda (50:52.914)
One of the four partners will take many of the calls, but I’ll take maybe half of them. And at the end of that, we invest in about three new companies for a week. So 300 becomes three. So it’s 1%. It’s 150 new investments per year, not including the follow-ons and the companies we already invested in. And of course, so we have a separate investment committee every week for whatever companies in the portfolio are raising, going public, going bankrupt, whatever, when we decide what to do. And we treat those as net new investments.
Knowing what we know now, the team of the company of the opportunity would we invest in? The answer is yes, we write a check, the answer is no, we do nothing, or if a secondary is available, we might take a secondary opportunity on the way up. And so that’s another maybe 7,500 investments a year. So total, we end up doing two to 300 investments a year, of which 150 are net new on average.
Harrison Faull (51:44.158)
Wow, you’re a busy man. But that is amazing. It’s great to see someone deploying at such scale, at such velocity, because the ecosystem need it. And they’re going to be able to leverage the ones that do pass the benchmarks that you require to get in as an investor, to get you on board, get such great value out there. It’s just,
Fabrice Grinda (51:45.914)
Hey
Fabrice Grinda (52:08.528)
Yeah, and look, and by the way, this is not because I decided, this is the best top-down way to maximize portfolio construction. It’s more a reflection of the founder, my partner Jose, and frankly, the other partners’ personality in us. It’s like, we meet people we like, we want to back them. And each founder is really tackling a problem. There’s so many problems. Like when you say climate change, it’s not one problem. It’s 1,000 problems. It’s like emissions at a cement.
factory at submissions when you’re extracting mineral. mean, it’s it’s a billion different sub problems and each founder is tackling one of them. And there’s as many, there are multiple entrepreneurs and solutions per problem out there. And so there’s a million or thousands of founders we want to back. And so it’s really reflection of personality, even though actually a diversified portfolio leads to the best returns in the business because of the power law nature of venture.
Harrison Faull (53:00.074)
No, it’s a passion. You’re pulling it through. I’m sure you convinced your LPs that they know exactly what you guys are doing, what you’re trying to build, and they’re on board with that journey. Flipping back to founders and advice to founders, given your experience with marketplaces, are there like three top pieces of advice that you’d give a founder who wants to build in the next marketplace for something. What should they bear in mind from day zero?
Fabrice Grinda (53:27.452)
first thing is it’s easier to build than ever before. So don’t overthink it. Just launch and build it. I’d probably build on Shopify, even though Shopify is more for e-commerce than marketplace. And you can then build the seller component on top of it. Don’t overthink the tech. Just keep it simple. Literally, I could probably build any marketplace today if I’m for less than $15k in like a month. Use Shopify. have companies doing hundreds of millions of GMV in revenues on Shopify. It’s not a problem.
It’s not where the key success factor is. The key success is can you make the unit economics work? Can you acquire the sellers and the buyers? Can you match them? Second big recommendation, probably the number one mistake marketplace founders make is they overwhelm their marketplace with supply. so when you start a marketplace, 99 % of the case you’re going to start with the sellers because they’re financially motivated by the platform.
If you kind of go to anyone in any category, it doesn’t matter where they’re selling. They could be selling a service, could be selling a product, and you’re like, hey, I’m creating this store. It’s free for you to be on it. I may have buyers for you. Do you want to be there? Everyone’s going to say yes. Like there’s a very limited cost for them to be on it. But if you just take everyone and you have infinite supply and you don’t have any buyers, then
Fabrice Grinda (54:47.026)
None of these are going to get any value out of your marketplace and they’re not going to have buyers. As a result, they’re not going to be active. They’re going to churn. If I wanted to build a locksmith marketplace in New York City, I don’t need locksmith there in New York. A couple thousand? I could probably call every one of them in a month and get them on a platform, but I’m going to have no demand for them. So they’re all going to churn. If someone places an order, they’re not going to reply. They’re not going be engaged in the platform. So instead, what you should do is you get the very best supply, a good price,
Good operator, depends if it’s a product or a service, but like the very best seller for that product category. And then like a limited quantity, and then you go find them a buyer, you know, spend money. And it doesn’t, I also don’t care what the channel could be. It could be influencers, be TikTok, could be Facebook, could be Google, could be sales team, could be inbound, irrelevant. Just make sure that the economics work. So you find them a buyer and you make them happy. And then they scale the amount of time and products that they put in your platform relative to others.
And once you’ve reached kind of saturated them, then you bring the next seller and you keep scaling your supply and your demand in parallel. You don’t massively scale one side before the other, unless there’s value in having more items, which are some categories you need a critical mass of items before you can actually attract buyers. Otherwise you’re going to overwhelm your supply side. Nothing’s going to convert. The sellers are not going be engaged and everyone’s going to churn. You basically, you’ve drowned your marketplace and you’ve killed all chance of liquidity.
So really scale up the supply and demand in parallel, making sure both sides are happy at all times.
Harrison Faull (56:20.188)
That’s great advice and not something that might become as intuitive to someone that hasn’t built a marketplace before. So thank you very much. Okay, so that’s the founder that hasn’t started. The founder that has started who’s not seeing the cohort performance,
Harrison Faull (56:43.698)
Okay, thank you. Okay, so that’s fantastic advice for the MVP, the founder that’s just about to start their marketplace. When it comes to a founder that actually has taken that step, has taken that leap, they’ve got a marketplace going, they’re seeing some growth, they’re seeing some traction, but maybe their cohort performance is not improving over time. They’re not seeing that next user purchase more frequently. Do you have any advice on what to do then?
Fabrice Grinda (57:13.074)
So obviously finding product market fit is the number one thing that kills or at least success in startups. All I would say is, look, if you’re 20 % away, you’re going to figure it out. You’re going to change the funnels in a way that you can get there. You’re going to get optimizations in your marketing channels, et cetera. If you’re 10x away, you’re probably not going to get there with whatever it is you’re doing today. You need to change something pretty radical. Product, user experience, business model.
distribution strategy, et cetera. if you’re far away from it, probably not going to get there, which is OK. You use that lesson and pivot into something else. And if you’re close, just keep iterating on whatever current approach you’re doing. Now, there are some things you need to realize is something solve themselves automatically through scale. So imagine your economics are underwater because you’re paying the delivery people or they’re being paid on the marketplace $15 an hour, and you’re doing one delivery an hour.
But at scale, you can easily imagine that’ll be three deliveries an hour, and so $5 a delivery, not 15. And there the economics work. Then you can still articulate why you’re going to get there. Now, understand this. VCs like me, want to growth. obviously, we’re not going to fund profitable growth, but not profitable as in you reach underlying profitability. Profitable, you did economic growth. So the objective of your seed is to go to your A. The objective of your A is to go to your B. And from B, then you can go to full-blown profitability.
But let’s say you’re a consumer facing marketplace with like a 15 % take rate. At seed, you’re probably raising the median right now, three and nine pre, and we expect you to be doing 150k with the GMV. And with that, again, 15 % take rate. So if you’re at 5 % take rate, you need to be 4x bigger or whatever, 3x bigger. With that, we expect you to be at 750k in GMV with a 15 % take rate in good union economics, like 66 % margin, let’s say.
for your A. And with that you get whatever 2.53 million a month in GMV for your B. Again, with good economics. So cohorts, we expect the cohorts to improve over time. So the more you go on, the more valuable your marketplace, typically the more valuable the community is, the more items you have, the easier it is transact. And so we would expect new users come in to buy faster, to buy more.
Fabrice Grinda (59:38.643)
and to have a retention that is higher. And so if pretty quickly you see that the new chords are worse than the old chords, it probably, may mean the market is swelter than you think it is because it suggests that you already got all the early adopters and then the rest are not that excited or interested in the category. yeah, chord analysis matters a lot. LTV to CAC models matter a lot. And also making sure you have density in your acquisition channels because
If you’re doing Google almost totally fine, make sure that you can spend not just $100K a month, but like $1 million a month, or $5 million a month, and then you keep scaling. You have proper network effects when your cat goes down over time. If you have real network effects, you start getting more and more organic growth. So your blended cat should actually be declining over time as you scale. If your cat keeps going up and up and up, again, it probably means either you don’t have network effects or the market is more capped than you thought it was.
Harrison Faull (01:00:35.072)
Incredible advice. Thank you. Okay. With this AI boom and tools that are so easy for people to code now, is there anything particularly exciting about applying AI to marketplaces that you’re seeing happen today that hasn’t happened before that could reinvent space or just help that founder put fuel on the fire?
Fabrice Grinda (01:00:58.534)
Well, first of all, every founder should be using AI to improve productivity in their startup. Like customer care, productivity can improve dramatically with AI. Sales, productivity can improve dramatically with AI. Programmer productivity improves dramatically with AI. So you should be using the AI tools. I I take that as a given. Now you could also use AI to improve marketplace flows pretty dramatically. In some categories, now you could just take a photo and the AI can detect the item.
Fabrice Grinda (01:01:27.58)
pick a title, write a description, select the category, select the price, say if it’s real or fake, like poof, in like three photos, 20 seconds, you have a listing. Compare that to the old school way of doing it on eBay, where you do all that work for yourself. It’s like 10 minutes to put a listing, plus you put a credit card details, et cetera. So you should definitely use AI to improve buyer and seller flows to the point that you increase conversion rates, basically.
Fabrice Grinda (01:01:55.739)
In some categories, it’s very easy to do, like trading cards or collectibles where the items can be recognized or unique. In some categories, it’s less easy to do and may not be in the incumbents, rather in a better position to do it than the startups because they have the data. So Rebag, which is a handbag marketplace, has all the data of all the handbags which one are fake or real and what price based on the level of scratches and et cetera. And so they’ve created their AI called Clair to help you list your handbag.
They can do it, but if you were just a startup starting, probably you don’t have the data to be able to do that. But there’s also third party AI tools that can help on the marketplace. So we’re investors in a company called PhotoRoom. And what PhotoRoom does is you take photo of an item, it detects the type of item it is, and based on the marketplace you want to sell it on, it’ll change the background image of your photo to maximize the conversion and sell through rate. So sometimes it’ll put a white background, sometimes it’ll put a nature or whatever. mean, so there’s a lot that can be done from an AI perspective.
And of course, depending on the search behavior, you can improve your search and your recommended listings like, you like this, you may also like this, through AI in a pretty dramatic way. these are the most fundamental ways to use AI in marketplaces.
Harrison Faull (01:03:09.843)
I really like the idea of investing maybe into a startup that needs marketplaces as a customer. So that photo room, obviously you can give them instant scale. You’ve got 1100 portfolio companies, many of which are marketplaces. Bam, instant go to market strategy.
Fabrice Grinda (01:03:21.266)
Exactly. We’re investors in TopSort. TopSort helps marketplaces monetize by selling ads to their own sellers, kind of like Instacart or on Amazon right now. You can buy ads as an Amazon seller. And so it increases your take rate and it’s very high profitable, very profitable. And so we invest in that and of course then we send it to all portfolio companies and it’s win-win. TopSort gets all of our marketplaces as customers and the customers get higher GMB take rate. So it’s amazing.
Harrison Faull (01:03:51.694)
Incredible. Look, Fabrice, I know we’ve already gone over, so let’s wrap things up and just end by saying thank you very much for your time. The wisdom is incredible. For the founders out there that want to approach you, want to get investment from FJ Labs, where would you prefer that they send you DealFlow?
Fabrice Grinda (01:04:10.652)
So if you want to learn more about my thinking, read my blog, fabricegrinda.com. You can actually talk to my AI, fabriceai, at fabricegrinda.com. So fabriceai.fabricegrinda.com to ask any questions you may have and that you approach me directly to send me deals. The best way is to send me a LinkedIn in-mail. And in that message, though, make sure you describe what the startup is, what traction you have, include a deck. Basically, give me every information I need to decide whether it’s for us or
If you just say, I have an amazing story, I’d like to talk to you about it, you will not get a reply.
Harrison Faull (01:04:44.0)
Thank you very much.