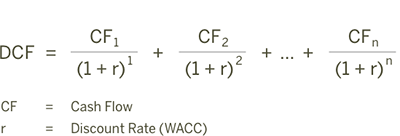I had a fun conversation with Mark Peter Davis of Interplay about my love of marketplaces and all things FJ Labs. The discussion was peppered with lots of entrepreneurial advice and thoughts on impact.
Their Episode Description:
This week I chatted with Fabrice Grinda, Founding Partner at FJ Labs. FJ Labs is a VC that specializes in marketplaces and invests in every geography in every category at any stage. As Fabrice puts it they do angel investing at venture scale, meaning they don’t lead rounds but do a massive number of investments every year. Last year they made almost 200 investments.
Fabrice is super interesting beyond being a VC. He’s been a serial entrepreneur for a couple of decades at this point and has interesting views on wealth and impact.
He started what was essentially the ebay for Europe and then OLX, the Craigslist for the rest of the world.
During our chat he shares some incredibly useful tips for entrepreneurs – especially for those who are interested in marketplaces. We talk all about his approach to venture capital, how FJ Labs operates and makes decisions and much more. Enjoy.
Show Links:
- Follow us on Twitter: @fabricegrinda, @mpd
- Guest Links: FJ Labs
- Guest Articles: Pandemic, Populism and Policy Failure – The Surprising Case for Optimism in 2020
- Podcast Links: YouTube, Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn
Transcript (this is an automated transcript):
MPD: Fabric, thanks for being here.
Fabrice Grinda: Thank you for having me.
MPD: I’ve been very excited to have you on I think you’ve got a lot of wisdom and you do something that most people don’t do and that you practice radical candor. It feels like in everything, every time I’ve ever talked to.
So I think we’re going to get into some really interesting topics today. And I think I have a feeling you’re going to share more than people normally comfortable with, which I think is very powerful. You’re going to help a lot of people. Let’s start though. Let’s level set this can you give an overview of FJ labs?
I think people need to know what you’re doing for your day job before we extend beyond. Sure.
Fabrice Grinda: So my current day job is to be the founding partner at FJ Labs which is a venture fund – actually it’s an accidental venture fund. It really came out of my angel investing activities while I was an interpreter.
So for the last 24 years, I’ve been building companies, I’ve been running companies and. Other founders kept approaching me for me to invest some of them. And for the longest time I thought they were, should I be doing this right? Is it a distraction from my core mandate as a founder to be investing in other startups?
And I’m like, if I can articulate lessons to learn to others it probably means I’ve internalized them. And so it’s okay. And meeting all these amazing founders beyond helping them realize their dreams is also an amazing way to keep my fingers on the pulse of the market. So by 2013, when I sold my last company, which by the way, was like dried or missing.
I don’t know if you want to cover that until I went, the last company was real quick. So the last company was a company called oh blocks. It’s today, the biggest classified site of the world. It’s a 11,000 employees in 30 countries. It’s the leading classified site in Brazil and all black tem and Russia, Ukraine, all of these sued Europe and India, Pakistan of all the Southeast Asia and the UAE and all the middle east.
And it’s basically what Craigslist would be or should be if it was running. By someone like me, meaning a modern UX UI, integrated payments and shipping and escrow. Exactly. No, no spam, no scab, no birders, et cetera. And actually targeting primarily women in a female friendly space, given that women are the primary decision makers in all household purchases.
That companies like over 300 million new users of mothers is absolutely ginormous. And after I sold that already at 150 investments doing really well already pulled them with my current partner. And I was like, I like building companies like invest in companies. Let’s create a structure that allows me to do that.
And I never really set out to build a venture funds. And I think by virtue of being visible, I started being approached by potential investors and said, Hey, we would like exposure to where you guys are doing. Do you mind if we co-invest with you? And so 2016, we took our first investor LP for 50 million, one LP outside of our own capital.
Yeah, it’s again, what I be basically they’re people that had it, it’s a company called . They were a big telco in, in Norway. And they had backed my biggest competitor when I was running about locks and ultimately we fought a big war and we merged 51 for us, 49 for them. And by then we, all of this I’d like unwell.
They’d made like a billion dollars and they ended up owning a whole bunch of classified assets around the world. And they were like, Hey, we love you. You’ve also made us a lot, lots of money. We’d like to understand what’s going on in marketplaces in the U S to either bring it to our markets or defend against disruption.
And so it was really both strategic for them. And financial in 2018 we raise fund two and they’re like, Hey, if you want to bring other people on board, why not? And other people’s sorta approaching us. So we started getting like a lot of family offices that were being disrupted by tech and a lot of other strategics were interested in investing in the category.
And so we finished deploying that and that was a hundred, 225 million finished uploading that in July of 2021. And then we close fund three, which would be like three, 400 million with either amazing founders that I’ve worked with forever, like Reed Hoffman, or, whatever Kevin, Ryan, or the founder of Wayfair or these family offices were actually strategics interested in either buying or investing leader seizures in the companies move us.
So I guess w w. That was a long-winded way to answer your question. So my day job is running FJ labs. FJ labs is an a, a venture fund specializing in marketplaces. We invest in every geography in every category at every stage. But the focus is we really do angel investing at venture scale. We don’t lead, we don’t price.
We don’t take board seats. We decide after two, one hour meetings, whether we invest or not with full transparency, we tell them why we’re investing, why we’re not investing what we need to change for us to change your mind. And we try to be as Frey, founder, friendly as possible. So we’re not setting the terms we decided very quickly.
And we’re super prolific. To give you a sense of scale to date, we’ve invested in overheat 150 startups. Last year, we invested in 281 startups, so 180 new investments or 101 followups, and it’s a lot for a venture firm and it’s been going really well. We’ve had 265 exits and so far in a 45% realized I are.
So things are good.
MPD: That’s great. Okay. So what’s the typical investment profile. Cause when you say angel investing at a venture scale, I get the angel investing part that your, the process is less rigorous it’s you’re looking at more strategic elements rather than doing your own diligence.
I get that nothing wrong with it. The question is when you say to venture scale, is that the reflection of the volume, the amount of capital you’re managing the volume, what is it? The check size?
Fabrice Grinda: Yeah the angel investing in venture skills really because of the overall. Capital deployment. We’re deploying a hundred million a year, 150 million a year potentially, but this funds which is way more than typical angels deploy.
Now, the reason it’s still angel investing is writing small checks relative to the lead. We don’t want to compete with the top VCs in the world for allocation. We want to be their friends. In fact, most of the deals come from friendly VCs or sharing deals with us in return. Of course, we send them all of our deals.
And so our pre-seed check size is going to be like 200 K or C check size, like 300 K or eCheck size is 3 25 or beyond words is 7 25. So it’s fixed check sizes that we’ll take lots of philosophers available and they’re always small relative to the lead. And that’s why it’s kind of angel investing in venture scale.
But I’m more than happy to talk to you and walk you through the process of how we decide whether we invest or not. If you’ve
MPD: teed it up, let’s do it.
Fabrice Grinda: Yeah. So actually, before I get to the process, I’ll walk me through the flow. These days, every week we get about 200 inbound deals and often many more than that.
And they come from three sources, a third comes from the friendly VCs and every eight to 12 weeks, we sit down the top hundred VCs in the world, covering every siege, every category of geography and we share deal flow. And it goes from everyone the amplifies or whatever first submitted to the pre-seed stage with the.
General catalyst, Bessemer Sequoia first walk in the middle, all the way to whatever the tigers at the leader stages, where we bring them all of our best seals. And in return Bain by to some of the deals where we have expertise. So mostly marketplaces about a third of the deal comes from fellow founders.
So at this point we’ve backed almost 2000 founders in the 835 companies. And they come back for their next company. They send us their friends. They’ve sent us their employees to becoming founders and about a third of the deals come in cold. And it actually, we review even the cold inbound deals and that 16% of the investments we’ve made have come from cold.
And some of the very best investments come from cold. So we get these seals they’re assigned randomly to one of the team members, unless someone says they want it. We we’re four partners, three associates, and one analysts. And we reviewed the deal we decide, is it appropriate or not for us or not?
And usually about. Three quarters of them are not there. They’re amazing, but they’re not for us. They’re like biotech, hardware, space SAC, and we don’t feel that we have appropriate expertise. So we review and we, the other 50, we take a one hour call and that one hour call, we try to assess four things and that’s actually the evaluation criteria.
Do we like the team? Do we like the business? Do we like the deal terms? And does it meet or pieces of where the world is heading? Now, let me double click on all four of these. Do we like the team. Every VC in the world will tell you. I only invest in extraordinary people. The thing is that’s extremely subjective.
What is an amazing team? And we’ve actually looked and thought through what it meant for founders to be very successful for us. It’s someone who is both a visionary and an execution machine. And that means someone who is extremely eloquent and as extraordinary communication skills. But that’s not enough because if you only have that, maybe you build a you build a very large company, but one that’s not profitable or it doesn’t scale, et cetera, but that’s, that is necessary.
It’s a necessary but insufficient condition. Because if you have an amazing, if you’re an amazing or rater or public speaker, you can attract better teams. You’re going to raise more money. You’re going to get better PR and you have better. But you also need to be able to execute. And we look at that, that we evaluated over the course of when our call is, how well do you understand the business, your hand?
How well do you understand you did economics? And we want you to be able to articulate even pre-launch, we want you to have done the lending page analysis and done a customer, cocky a customer acquisition cost analysis, and compare that to look at what the average order value in the industry is.
See what the net margin structure you’re expecting is. And you should be able to articulate that intelligently and the Venn diagram of people that are amazing storytellers and people that are amazing at execution is actually the intersection is very small and we want people that are both number two, Businesses that are compelling.
And for and so for many, some VCs, by the way, number one is enough. And if you’re pre-seed, pre-launch obviously will, this is the most relevant metric once you’re post-launch actually we do care, but the other three number two is, do we like the business? Which means for us, is the category large enough?
Or can it be larger enough through your execution and, or the unit economics is compelling and we are extraordinarily unit economic driven in marketplaces. And obviously this a little bit different if you’re in e-commerce is a little bit different if you’re in SAS. But we try to invest in businesses where you re.
You’re fully loaded customer acquisition costs on a net contribution margin basis after six months. And we’ll use three X your CAC after 18 months now. And ideally we don’t know what the LTV to CAC is because you have negative churn. In which case, who knows it’s 10 to one, 20 to one, et cetera.
And if your unit economics are underwater, which can happen, we want you to be able to articulate why with scale. They will automatically fix themselves. Maybe you’re in a food delivery business. And right now you’re doing one delivery per hour, you’re paying $15 an hour. Your delivery guy, your unit economics are under water, but the minute he does three deliveries an hour, it’s $5 a delivery.
And it works. Something like that. Like I don’t, it should not require every story. The multi-payer so align for you now, economics to work. And we really care about that because otherwise you may build a very large business that doesn’t make any money, which in the long run doesn’t really work out. Number three, what are the deal terms?
And we are. Yeah, nothing’s cheap and tough, but we want something that’s fair. In light of the size of the opportunity, the quality of the team, the traction that you have,
MPD: what is fair? How do you think about that?
Fabrice Grinda: So evaluations went up, especially in the late stage last year and, something I covered in one of my macro articles, but the median pre-seed the median valuations didn’t move up nearly as much as you might think.
And crypto falls a little bit of time that route, but then the median pre-seed for us until 2020 was like three to five pre raising one. And last year went up to six, seven, but not that much more. And so if you’re, pre-seed raising a 30, more likely than not, we’re not going to do it. The median seed used to be like re three raising at eight and nine pre and last year we went up to 12 and that’s still reasonable for us and the median a, you used to be, you’re raising seven at 22 and iRacing 10 at three.
And those are fair by our standard with relevant traction. So as your seed ran, we’re expecting you to have whatever, 150 key in GMV per month with a 10 50% take rate of the, a Rand, you’re doing 500 K in GMV and the B round, you’re doing 2 million GMV per month, more or less, it depends on the take rate you have, et cetera. Now there are exceptions, right? Like the rounds you’ve been reading about in the press are like, oh, they raise a $50 million series, a two 50 pre total, and these crazy. But yeah, we wouldn’t do those deals. There were amazing for the founders and the companies that actually I can make an argument.
Many of the companies that dies because the company, the founders raise too much money at too high, a price. They don’t grow into that valuation. And that kills the companies because of like anti-pollution provisions and it one more Sudan, Rams. It’s really one of the top reasons companies die is founders raising too much money at too high a price.
So we don’t do these deals. So the mean by the way is way higher than mean seed a and B is way higher than numbers I gave, but the media actually is not. And we’re so prolific. We have a good sense of where the market is. And so we stick to our with the exception that if you’re a returning founder for us, that has done well before we will back you, no matter what, no matter where you build, no matter the raise, et cetera, you don’t even need to take a call.
We’ll just send you the check. And so we have done a few crazy deals by that’s the reason it, also many of those deals are out of scope for us. Like we had the founders of a. Vettery, which was a labor marketplace then decided to go. And we sold a deco for a hundred million made of whatever, 8.5 extra money.
Everything was great. And then they went on to build Archer, which has an electric flying taxi company. And they’re like, we’re launching we’re pre-seed, 80 pre or whatever, a hundred pre. And we’re like, okay, here’s the check
MPD: is those is the re-upping founders, your lumps,
Fabrice Grinda: Ever increasing because we have 2000 founders, we backed, put it differently.
30% of the portfolio is non marketplace. And many of those are the re-upping founders which is a good sign that they have they’re coming back and they would have worked with us. But we also do like tools around marketplaces, et cetera. And we’re doing a lot of stuff. That’s like an interest things that interest us, which actually leads me to selection criteria.
Number four is your idea in line with our thesis of where the world is. And we are extraordinary thesis driven. We have a clear thesis on the future of finance, the future of food, the future of see the future of automotive, the future. And even within marketplaces, we have three core thesis on marketplaces that we look for and we want ideas that are in line with that.
And in a way we’re also mission driven, right? The reason I’m a VC, the reason I’m an investor is I, the world is facing a number of fundamental problems. We’re facing a climate crisis. The, we have a social inequality and inequality of opportunity or social injustice. We have a mental and physical we’ll be in crisis.
And the, I do not think that a. The political system is going to address any of these. And so it’s up to us as founders to use, to be solutionist to use technology, to find solutions to the world’s problems. And so it is mission driven from that perspective. I want to try to invest in companies, founders that are trying to address these fundamental problems.
And by the way, the bigger, the problem, the bigger, the economic opportunity, and it fits better in a for-profit model because this actually ends up being more scalable and more effective. And here we have it. If we’d love the team, we’d love the business. We’d love the deal terms. And we think that the ideas in library, their thesis, we invest and we can decide that in one hour.
MPD: That’s great. What’s the what are the reasons why a founder should choose to work with you guys? This is my underhand pay.
Fabrice Grinda: And take a swim, the were former founders. So we actually know what it’s like to operate a business and we can talk extremely intelligently about the complexities of operating a business.
We’ve probably seen more marketplaces than anyone else either. And in addition to the fact that I run marketplace, I’ve run marketplaces for most of my life. And so when it comes to everything from like building liquidity, do you start with the supplier, the demand, should you go hyper-local or national or international?
W should your rake be 5% of 1% of 20% you’d have, how do you measure it? Let’s see supply demand. We’re probably more. Versed. Any other investors out there in this category in terms of being able to help you and last but not least, we’re in an ma because we don’t lead and we don’t price. And we have these amazing connections with all the other VCs, we will get you funded.
Like our superpower is we will get, if you need help raising your filling this round, we will do that for you. And more importantly, and most people do not need help raising a specific, the ran they’re typically talking to us about but if they, when they go to the a, when they go to the beach and they go to the sea, we will ensure them to whomever, like first of our grade lock and Driessen whomever is right for them.
We will make the intros and is extremely valuable for them because it directs the fundraising and makes it a lot simpler. We will give them feedback on like them, but back on the pitch on the process. And it’s also super efficient because you’d we have 850 companies in the portfolio and yet.
We’re often the most value added investor these founders have because we really focus on when to help them, we’ll do, we’ll help them right before they go fundraising the next ran and that’s the most valuable for them.
MPD: Okay. So there, there is a implicit piece of this that I think is the most interesting.
It’s the sheer volume of your portfolio, right? There are a couple of firms out there that have huge volumes Techstars. My buddy, over at David phone number Techstars has a huge volume. He’s had a very different model than you. You have a huge volume. It’s not as common. Most firms are going out there and targeting 25 deals in a portfolio.
Is something there about what is your thinking around the optimal volume in a portfolio?
Fabrice Grinda: First of all this is a reflection of my personality and not there’s no intelligent portfolio construction. So I actually have done the research. And what is the ideal portfolio construction by the portfolio of F J labs is completely built.
Bottom line. We meet people. If we’d like them, we invest. If we don’t like them, we don’t invest. And at the end of the year, the chips fall where they may, and it just so happens. Of course, there’s more seed deals and ideals, more aid deals and deals and CDLs, there’s more U S deals than European deals or European deals in India and Brazil deals.
And so if you look at our portfolio for a number of deals for of, we’re mostly seated a then a few B’s and very few season and not too many pre CD there. And then we’re 55% us Canada. We’re 25% Europe. We’re 10% Brazil, India. We’re like the rest of the world and really all over the world.
But it’s not by design. Now in terms of number of deals to answer your question specifically, is I diverged on portfolio construction. The I actually I think there are many problems to solve in the world and I like finding ways to address many of these because we choose not to compete with the major VCs.
We could actually not run a concentrated portfolio. So first of all, by design, if I wanted to invest in 30 companies, I would need to be a lead and I would need to ride like five, 10, $15 million trucks. Then the entire strategy. Of working with the other VCs and being their friend and other competitor becomes invalidated.
But more importantly, as a reflection of my personal philosophy, I just like, meeting lots of interesting people and being exposed to all these different areas. And I get I, now I have a great sense of what’s happening in like everything from climate to to automotive, to real estate.
And I think it’s fascinating there also the corollaries between these other industries, which are the marketplace dynamics so much closer to people suspect. I find that fascinating. And so it’s more a reflection of my personality, but that said there is data, but what is the correct portfolio size and angel listed and analysis of what your return profile looks like based on the number of deals you have.
And basically because venture follows a power law. The best deals return, do most of the returns you need to be in those best deals. And the best way to be in those best deals is essentially to be in every deal. And so the angel was study, which actually was published in peer reviewed and all that is the more diverse your professor of your portfolio, the higher your IRR and your returns that you should invest in all qualified.
And they have a definition of what qualified beans deals possible. Now, the reason most VCs are not built that way by the way, is actually driven by the LPs. So LPs heat that diversity. Because they see their jobs as themselves picking the VCs that are more specialized. So the LPs are like, oh, I’m going to have this fund.
That’s going to be my series, a B2B SAS company. I’m going to have this one. They’re going to be my series B DDC e-commerce in Europe, whatever. And they do, they’re like little funds of funds, strategy and fund that does all that for them. They really don’t like, because in a way it’s like the job they should be doing.
And so LPs are not super keen on that diversified strategy. And so it wouldn’t work for most, but it really works. And the benefit is over longer periods of time. We’re always going to be in the title. That’s solid before now and anyone fund life, by the way, we’re never going to be top decile because if you imagine a fund, eh, is hyper concentrated, they do 10 investments.
One of those is a hundred X. They’re going to be at a 10 X funds and they’re going to be topped us all, but they’re going to have massive variability, next fund they’re 10 may not hit and they made Richard money. And by the way, most VC funds actually don’t return cashflow cash money beyond the S and P the top Cortel does.
And the top quartile is actually highly correlated over, over fund life by most do not it our case. We I’ve been, if you include all of my history as an angel investor and but not as a founder, right? I’m not including my benefit. The equity I got into companies I’ve founded on the 270 exits we’ve had a 45% realize I are over 24 years either.
That’s I don’t know where that ranks. It has to be in the top 10%, maybe in the top 1% over that time, Peter.
MPD: Given that you’re diversifying so much, is the core value add more sourcing or is it more deal selection? Because one of the things, theoretically, arguably the best portfolio is one investment, all the money in the world and the best company, the best returns, that’s it.
But the presumption there is that someone could be a good enough deal picker and get access to it. The core issue for a lot of VCs is they’re not great deal pickers. So how do you think about this? Is that the message to LPs like, Hey look, we’re good deal pickers, but we really don’t have to be because we play the game so broadly.
Is that part of the narrative for you?
Fabrice Grinda: Not really. So we were actually would argue we’re very good deal pickers. We will buy often. We will not be in the top 0.1% of deals by the way, because we’re so sensitive on price. And we’re so sensitive on unit economics, either like we would have passed the Facebook, we would have fastened Google because neither of them had business models when they launched, nor could they articulate where those models, the, those those models were.
But we have a lot of singles and doubles and triples. So even though our portfolio is so broad, we’ve actually made money in over 50% of our exits which for a seed, mostly seed fund is extraordinary. Last year we had 41 exits, we made my name 24, we lost one in 17. And obviously you make a lot more on the 24th and you lose on the 17.
So I think we were very good pickers, number one, but two, obviously our deal flow is amazing because we built a brand as these founder friendly. Guys who’ve decided after you investor died, who were super helpful. And if you’re doing anything marketplace related, by the way, marketplace, let me define it pretty widely as if you’re building something that’s an intermediary between a seller of something and an a at a buyer or something.
And that thing could be anything. So to me, most of FinTech is the marketplace because, think of Clarita. It’s an intermediary between providers of capital. Typically the banks will give you the lines of credit and consumers that are borrowing. And many people wouldn’t think of it that way.
But to me, those dynamics, if you’re matching sellers, the buyers, regardless of the category it falls in the marketplace definition for us, which is obviously why we can invest at 300 marketplaces in a year.
MPD: Okay. So there’s a little bit of learning here. I think you’re a bit of a pioneer in this type of volume for something outside of an accelerator incubator model.
Yeah. Whereas this model gone wrong that you had to correct. What did you learn along the way? That’s nuanced to not being a VC and not being an investor, but being a high volume VC or high volume investor,
Fabrice Grinda: The way luck what’s I don’t know if it has gone wrong in the sense that we can typically.
First of all, I don’t think it’s necessarily easily replicable by most because we are in extraordinary privileged position to answer also part of the previous question where the deals come to us, right? Like most associates and analysts and most VC firms spend their time like networking and finding deals.
In our case, we’re like drinking at the fire hose of incoming deals and we’re reviewing the incoming deals and we would like to do more at boundaries, just we’re too busy, previewing main band. And we have the 200 Ben bands. We’d there’s. Yeah, we do miss seals as a result of that. So I D we are trying to change that to some extent, even though, so first of all, there’s the, part of the reason I can share my entire strategy online, including everything, the deal memos, the philosophy, et cetera, is even if you had all of it in your mind would encode it, even though probably hard to do without the 24 years of like ad bats of seeing 5,000 companies a year without a deal flow.
So I really replicable now where it’s gone wrong. Yep. Sorry.
MPD: And as I say, FJ labs is a
Fabrice Grinda: marketplace. Yes, we are our marketplace. Absolutely. We’re matching founders with money, from our LPs. And by the way, our LPs I’m the largest LP in the fund, right? Like about 450 million we’ve deployed to date, over a hundred million of that is my own money.
Maybe one 50. I actually, haven’t tried to look at it too closely because this started as a frankly personal investments for my partner. I said myself again, the accidental VC thing. One more thing. I know, I didn’t answer the question. One more thing we do very differently by the way is the following.
So we. We don’t reserve capital for follow-on. So we’ll invest that of whatever fund is currently active. The follow-ons. So we tell our, because we don’t always follow on we’ll evaluate follow-ons as though they were new investments, knowing what we know now, the company of the team would the terms, would we invest?
And often the answer is we love the team. We’d love the company, but the valuation is insane, so we’re not taking our Paratas. And so we’re, we’ve been following on and maybe 33% of the deals. But as a result, it doesn’t make sense to reserve capital fellows in a fund. So we do it in other funds, which leads me to the issues in a way we face, right?
Like the problems we face. As we have had a really hard time, much harder than ever to expected raising capital other than the capital that keep to us automatically. So we’ve had these LPs that are like friends. They’re like, here’s a check, they know
MPD: you were, I know your success,
Fabrice Grinda: those exactly, or strategics that we’ve worked with from across many years who want to exposure where we do or family offices.
And so there, the capital’s come, but pitching institutional investors has been really so far. We don’t have a single institutional investment partner differently. They don’t love. Anything about what I just described the hyper diversification, because they feel that in a way it’s their job to find different funds that cover different areas and hyper diversification number of deals.
They don’t like that. We’re multi-stage, they don’t like that real multi geography. They don’t like that. The follow on strategy is in whatever fund is currently active in which versus, having capital reserve followings in the original funds. And so all of that. And so it’s been, it’s taken way more time to raise capital than I would have liked.
And also as a result, we’re proudly a much smaller fund that we should be. So right now, we’ve closed for student 10 million of the new fund and you find. It’s three to 500 million, five, really a hard cap. I would like to hit it, there’ll be at least 300 million and it’s been seven months.
It’s mostly the existing investors. Re-upping yeah, there are new investors like founders that we’ve backed that have excess exited that are investing in it, et cetera. But again, we have, don’t have a single institutional investor in the fund because of all the reasons I, and I’d like to change that because the reality is we should probably, we could be a billion dollar fund with no problem.
Despite the not leading, not pricing strategy with given the volume we have if you do, if I do intelligent portfolio structured, like what is the maximum size I can deploy at pre-seed without leading to 25 K or so maximum check size, I could deploy at seed without leading it’s four 50 at AA could probably write a million.
That’d be, I could probably write 2 million and let’s see. It could be right, probably right. 5 million and up to 10 million in like the pre IPO Rams. And so if you look at all the deals last year, all the allocations we had, we could have deployed 350 million. And yet we didn’t have that level of capital.
And so we only deploy a hundred million. So what we’ve done to not run out of money after a year because our LP base is not such that I can actually. Say, oh, instead of three years, we it’s just one year and now we are re-upping they don’t want that is at nor could I, because I’m the biggest art piece.
It’s also driven by my personal cashflow. And so what we did instead is we men decrease her check sizes to not run out of capital. So currently, as I said, our HX size is 3 25 K. It could be a million or beach, X size is 7 25. It could be two and her and frankly, DHX license. So the 25 K and could be 10.
And so that’s been an issue I’m trying to address it and we’ll see if we were successful in the future now, in terms of underlying performance and access to deals, et cetera, Matt, I think B hasn’t been too much of an issue, I guess the other issue, it’s something we’ve learned as we’ve had to build a very big ops team.
The team we’re 30. Which is a lot of people are most people
MPD: doing, cause it sounds like 10 or so those are investment professionals. What do they, yeah,
Fabrice Grinda: so yeah. So four partners, three associates. Why now? So eight investment professionals we have two but then we have a big back office team or like the head of operations, the CFO the lawyer, the, all the accountants and the that are in the back office team.
And then we have all the support team for them. So when
MPD: you say 200 deals a year, you mean 200 pounds of paperwork?
Fabrice Grinda: Yeah. Let’s do a lot to do. Yeah. Everything, stock, purchase agreements, follow ons, legal approvals, exit, there’s infinite back office work to do. And actually one more thing we haven’t done is we’re currently not gap dot a gap accounting, because like, how do you do gap accounting on.
800 startups and we don’t even, we want to be the founder friendly guys and so doing an evaluation of each company in the portfolio when they’re like seed is a massive exercise that most, firms, which is another reason we haven’t been able raised institutional money. And maybe we need to have bite the bullet and do it.
In fact, we’re currently talking to Mike CBO and YC and, people like that, like how do you guys do it? And we probably need to buy that bullet at some point. But yeah it’s a lot of the issues that like you don’t think about when you’re dealing, when we’re lower volume from,
MPD: okay, now you guys are the marketplace experts, and that’s very clear what are three rules of thumb that marketplace entrepreneurs listen to this need to know the things that are like, Hey, these are the baseline pro tips, right?
Fabrice Grinda: When you’re building your marketplace and you have your chicken neck problem the. Place to start is with supply because the sellers on the platform are financially motivated to be on the platform. And I would go to them and set said, low expectation and saying, Hey, we’re launching this. We’re free to launch at the beginning.
And we take just a rake, a B in there, but here’s the key. And here’s the pro tip. It’s easy to have infinite supply, but if you’re drown your marketplace and infinite supply and you’d have demand for it, they’re all going to turn. They’re not going to be engaged. So when you launch, you curate the very best supply for it in one vertical, in one category, maybe even in one geography, like in one zip code, and then you find demand for that.
And first of all, there are the very best. So you make sure they’re engaged. You make sure they understand where the product is. You understand what their needs. Then you find demand for them, whatever way it is. It could be sales driven. It could be marketing, it could be Google, it could be Facebook. And by the way, I actually like paid marketing to work because that means it’s scalable kind of infinitely you find demand and what you wanted to get to for that supply.
And again, very limited supply, highly curated. You want to represent. If it’s an item for sale, you want the probability of the item for sale to be about 20, 25%. That’s when you have pretty good liquidity, if it’s a services business, you want to represent at least 20% of the revenues of that provider.
And then once you have that at that scale, then you scale the supply up one more like whether it’s in the same zip code or gee sitter, adjacent category, and then you match. So you always, you start with supply, you bring them in and then you scale both always in parallel. A problem is it’s so easy to get supplied that you could launch.
I could launch a locksmith marketplace and put every lots within New York on it, but then you have no demand for it. And so the supply is going to churn. There’s gonna be no engagement and the users, we awful, et cetera. So doing that is, is key. So that’s I guess somebody human mind or like magic trick number one, magic trick.
Number two is, as you start thinking about. How do I monetize? How much do I charge? Who do I charge? And what is the correct percentages? Because you see marketplaces like stock photography, marketplaces that takes 75%. And then you have some B2B marketplaces where it’s essentially 0% rate or 0.1% because of extreme price sensitivity.
And so the correct way to assess that is you look at the less toxicity of supply and the less, the city of demands and you take your rake on the more and elastic part of the curve. And the more elastic it is, the higher the rake is that turns out that in most cases you can take 10 to 20% from the supply side, but it’s not a hardest at roll.
It really depends on how fragmented your supply and demand is. And by the way, the more fragmented it is, the better it is for you as the marketplace, right? If you’re in a market where there’s three or four suppliers and three or four consumers, You’re probably not a marketplace. You’re probably a distributor.
And your ability to price and take margin is going to be very limited. And that’s why I be very careful of playing in like highly concentrated industries. It happened to me and not really a market place, but I was I ran a company that was selling ringtones to the mobile operators.
And in the early days it was okay. But like between 2001, when I launched in 2005 and my mom, I sold in 2004, but 2005, when I left all the operators, consolidated merge with each other, like singular with, at and T Verizon with they’ll remember whom I’ll be like. And also when we went from. 50 customers.
So four and on the music come to a five and on the music company side, they all merge with each other like BMG and whatever, and EMI and whomever. And they also went from like many to three or four. And so all of a sudden there were four and five and it wasn’t an issue until we had 50 million in annual revenues.
But the minute we hit 50 million annual revenues, we started being seen by the VP level at these companies. And they started seeing us in their P and L and they started squeezing and squeezing. So in 2004, with my company, we did 50 million in revenues and 4 million in profits. In 2005, we did 200 million revenues and seven and eight in profits because they basically divided by our margin by three.
And so that’s not a marketplace, you’re a distributor, you’re a facilitator, but it’s not a proper marketplace.
MPD: Okay. So now you guys do more than invested FJ labs. I know this is evolving. You guys have been a studio, right? You’ve been building companies. You don’t talk about what you guys do when the method for it.
Fabrice Grinda: Sure. The reason we were a studio is really, I say, bang. It’s what do I like to do? I like to build companies. I could invest in companies. I love that. And so every year we’d be coming up with ideas and it was like, try to build them either personally and go run them, which I did for a few of them or with entrepreneurs and residences.
And we created through happenstance, a program that ended up being successful. So what happened is. I don’t even remember the year, maybe 2010 or 2011. This young founder reach out to me and he’s Hey, I’m McKinsey, Harvard business school. I am I’m at HBS right now, but I’ve raise 500 K and trying to build this company.
And Eddie kept harassing me. The thing is I was running billing oil, super busy writing a relaxer. I’d like, so that 10,000 employees in 30 countries, and I was getting emails like that, like dozens every week. So I ignored him and ignored them. And one day he’s Hey, I’m at the door of your office, can we meet?
And I’m like, okay, maybe I’ll beat him. Maybe I’ll leave. Let me be. And he was building like some sort of chat roulette for competitor, and I’m like, terrible idea. Won’t work return the money to your investors, call it a day and. Cultural back the next day. He’s oh, thank you for the radical honesty and candor to when I’ve been like honest with me.
I talked to my investors, I offered to return the money and they said, no, let’s find an idea. And another idea. So now why don’t you and I look on fighting an idea together. I’d have I’d like to know the last thing I want to have time. And I kept saying, no, I kept saying no. Then he emailed me a check for $5,000.
He’s I’m going to pay you $5,000 a month to work for you. And I’m like a fight. Keep your money. Yeah. You’re super motivated clearly. Let’s let’s see if we can do this. And in a way it it was useful because it forced me. The first thing I made him do is help me filter my inbound deal flow.
And at that time it was 200 a week. It was like 40 a week. And I was like, can I teach someone else? Might Euro six K I could have fight how to evaluate a team, how to validate if the business attractive, what my thesis is what appropriate deal terms are. And can I have him, do that for me and not pass the next Uber and turns out that while he was useful, because it forced me to structure my thinking on what my Euro six were and teach them to him.
And once he started seeing all the deal flow, he started getting ideas, sorta applying the same criteria to his own ideas. And then we started 50 ideas then became 10, then five and two, then one, then we pivoted and that company became adore me and adore me is a laundry DDC, commerce subscription company, both econ not which today is I don’t know, over 200 million revenues, I don’t know, 20 million tickets.
It might be much more than that, but I’d like at least that and crushing it. And the last thing he did. And I told them too, it was like, find me your replacement. And so we started a program where we would go to the first year of business school at Harvard MIT, Wharton, Columbia, Stanford, we’d say, Hey, you’re S you’re going to join us.
Full-time during the summer between your first and second year, half the summer, you’re going to be taught venture capital. Not because we want you to be VCs, but because we want you to see where the ideas are, how to pitch how to write a great effective deck and keep your pulse on the fingers of the market, your fingers on the pulse of the market.
And number two, pap the summer, you’re going to be in the company we’re currently trying to build. So you understand what it’s like to be an early stage founder, that profile. So the reason we took these schools by the way, even. On average, we’d rather have people that don’t go to business school.
It’s frankly, it’s just an easy filtering mechanism. And, but we only wanted people who wanted to be founders. And most of them, the profile was they were product managers or city managers of one of the larger marketplaces, like Instacart or Uber or or Airbnb. And they want to now go and do it on their own.
And and there were an HBS like looking for ideas and maybe improving their skills that like finance, something like that. So they join us for the summer during their second year they’re part-time 15, 20 hours a week. Mostly helping us filter inbound deal flow. And then when we graduate.
They become full-time EIRs meaning we pay them. I don’t know where the salary was, like maybe 135 K years. I’m like that to look for ideas with us, they look for their own ideas and we meet like on a weekly basis to iterate. Now, also every twice a year, we bring the entire team investment team, everyone like in the team together once in February and once in August and July, usually my house interest in kaikos who are in Canada.
And we have to all come up with ideas that don’t exist in the world of tech that should and out of these. And we usually come up with like a hundred, a pop or 150 up opposite, two to 300 ideas a year of which they can actually go and go deeper and pick some of these et cetera. And we typically would take two weeks.
I bet there’d be some churn because some people decided to build companies that were not, for us, some people decided they don’t want to be founders after all, et cetera. And we ended up building a lot of companies like that. We some successful some not so much. So we built a company called BP, which should have been Carvana, raise 150 million and was worth 700 million in like in famously blew up.
We, the main mission is we try to have the founders fail fast. So we try to build a company. We build a company called punch show, which is like an entrenched company and it didn’t grow big enough. And so we decide close it, but then we’ve had a lot of companies that are really doing well. So we’re in Rebag, which is a handbag marketplace.
I think they’re going to do 200 million of revenues this year and I’m like that that is that the founder is amazing. We were in properly, which is a Zillow Trulia meets compass meets a open door for Canada. Absolutely crushing it. Last round was like, multi hundred billion dollar valuation we’re investors
MPD: in that with you great company.
Fabrice Grinda: Yeah. Yeah. So I’m chairman of that one and unsure is one of the best a EIRs we’ve ever had also we’re the best founders we’ve ever had. The team is amazing. We’re in Mundey, which is a trade finance company between Mexico and the us helping us and B some Mexico export of the U S and there, they grew from zero to like tens of millions and originations in a year and a half.
Like my, my, I know that it sends really definitely over 10 million might be over 20 million now. We’re in like Seafair, a marketplace for helping shipping companies find seafarers, a work rise for shipping where we’re in a umami card versus vertical. And grocer in the Asian category, we’ve created Milko, which is a kind of Shopify for restaurants, helping people build digital brands in food and helping them operate restaurants operate better and more effectively.
Many of these that actually I ran one of them for a while, actually to 2014, 2015, I built a mobile classified site in the U S called Salud, which I then merged with wallop pop. I ran Walla pop. USAA was true, but a wallet pop. And then we merged that with let go, which now of course has merged with offer up.
So now it’s offer up and that’s a multi-billionaire company, which I ran in 20 14, 20 15. And the CTO model is as follows. Very different, very generous because we do very few. We, you come in, we pay you 135 K until you find idea, once you find the idea we put in the first seven 50. With 65% of the capital going to the team, 35% to us.
And then we commit the next 2 million at either 10 million valuation or market, if you can get better terms but we have the right invest 2 million in your next round. And and so the T it’s not at all, like some of the other studios out there where the teams get five, 10, 50%, or in our case, they started at 65% and actually real capital, right?
Like you guys have got 2.7, 5 million. So if you don’t want to go to market for the next first two years, you don’t really need to. And that model’s really worked well. Intrusive, like it’s fine. We build amazing companies. The problem is it’s time consuming and my time is not scalable. I’m still, I’m on the board of and these companies it’s the opposite model.
We’re coming up with the ideas. And often I even rent product like Rebag and lofty. I was like, I went to Ukraine and Romania and I hired the team. I re I was like scrum master. I was like, I was actually writing the stories and managing the teams. I was working day and night for them for many years.
And now I’m still on the board of like most of them ones I just mentioned. And so that model, it’s amazing. But it’s just too time consuming. And so putting that on hold for now, but we still have two or three more to build. We still have two more to build as we speak, despite the fact that we’re not recruiting a new batch and in 20, 22
MPD: only so much for breeze.
That’s a lot of sounds like you’re spread pretty thin if you’re doing.
Fabrice Grinda: Yeah. Yeah. Plus we have a SPAC plus the a week plus I do a lot of stuff in crypto, independently. What we do at FJ yadda I’m spread too thin as is. And so my current what I’d like to find a way to do while I. The reason I built the team to 31 is actually to do all the, a lot of the stuff I don’t like to do, which the good news is that the problem is when you’re going to something, the world sends you, the universe sends you more of that.
And so the temptation of course is to do more and more. But I need to find a way to be more scalable. And I think putting aside started the studio to spite of how much fun it is, eh, and just focusing on the venture side because it’s more scalable and POS probably more useful for humanity in the long run, but in terms of like placing bets in so many categories to try to address it, all the world’s problems is broadly a better allocation of time.
And I can tell
MPD: you’re inspired by it. Yeah. You’ve had a lot of success. I think that’s safe to say maybe an understatement of the day. Did you grow up.
Fabrice Grinda: Yes and no is the, which is a weird answer. My great grandmother so I greet great grandmother in the late 18 hundreds inherited a hotel from when her husband passed away.
And instead of doing the done thing and and marrying again, she had decided to just take over the hotel, which was like fully embedded. She turned it around, made it super profitable, then bought another one. Then another one, she ended up owning all of the luxury hotels in nice owning half of the residential real estate of niece, basically becoming the wealthiest thought.
And if not the wealthiest, one of the wealthiest women in the world in the late 18 hundreds She gave it all to, she had multiple children, she gave it all to, or oldest Augustus who was actually an effective manager and didn’t lose any of it, but a force by the time. But he didn’t do the same thing.
And by the time. It’s kissed took over. It was split between all of them and they all spent basically the new VAR reach. All they want to do is hang out with the queen of England and the prince of Monaco. And by the time of my grandparents’ generation, by the time my parents came along, there was basically nothing left.
And so the, I imagine a generation that had been brought up with the idea that they were going to be wealthy, never need to work. It’s the silver spoon in their math, and yet didn’t have anything already be to show for it. And so my father had started from scratch. So when w we were living, the four of them.
Brother and I have two brothers, so I’d like when we started at my brother and my parents, like in a studio apartment and he started working for this French billionaire as an endless, and they’re a leveraged buyout firm in the seventies. And so we came from, even though we had come from family that had a lot of money by the time my parents level, there was nothing left.
And so we started with nothing. I went to public school but in 1989 when I was 14 my father’s father was became grossly of the ranks. We can to CEO of the company that that, that guide bought through an LPO. And they sold it for whatever, like a billion dollars. I think my dad had a 5% of it in stock options.
And it’s like the pre not venture capital per se, but like a similar model and overnight became wealthy. And actually you retired at the age of 41, which I think was a huge mistake. But I guess it didn’t live through it because I, at that point I’d already, I was living with my grandmother and niece and then I’d left for college and probably out of ego.
I decided I didn’t want to take any require, ask for any help. So I paid for college. Most of them, I saw, for my living expenses myself. So I had to work. Like I went to Princeton and when I was 17, but I’d like to work four jobs plus build my first company to pay for it, et cetera. Whereas probably the easier thing would have been asked my parents for money.
So because at that point of time we did have money. Cause that was two years after my father had become wealthy. But because I had left kind of my parents, I was living with my grandmother. I also didn’t really notice a shift. And so I came from an upper-class family that was probably middle-class in income.
But that rose through the ranks. And then all of a sudden became wealthy at the. A 50 for me by my parents. My parents are getting,
MPD: but from a life experience standpoint, it sounds like you had more modest sensibilities as a kid than maybe generations before you what’s. How has money changed your life now because you’ve had tremendous success?
I know that is challenging for a lot of entrepreneurs who are going through these cycles. What have been the ups and downs of this evolution for you?
Fabrice Grinda: I don’t know first of all, as a kid, I was just built differently from everyone else in my family. I was like really serious, like until post-college I was like Shelton, for me it was all about like intellectual pursuits and getting a pluses and skipping all the grades and winning the Olympiads.
And I was completely antisocial not at all a good public speaker or. Just different. Like I cared about like studying economics and philosophy and getting a pluses and nothing else and map like no interest outside of that. And no time for anyone, including by the way, my family, I was extremely arrogant and condescending as a kid of you guys are not smart enough and worthy enough of my time and attention, including my parents, by the way, I was like, so it’s funny because in a way I was the best kid ever, like always a plus is going to bed early, not doing anything bad, et cetera, but it was also.
At difficult kid in the sense that I’d like, didn’t provide much love. It was like, yeah, you guys are not smart enough for me. Leave me be I’ve learned. And it’s interesting because I have come to value people, I think as you’ve you put the emphasis and value and things you were really good at.
And of course that I was really good at being smart and not so good at anything else. And so of course that was my prison by which to value the world. And as you become older and also more confident and successful, you’re also realize there’s so many ways to be and to live. And it’s not my ways a personal value judgment, but there are many other ways that are absolutely amazing.
That to answer your question directly it’s a little bit of a non-sequitur know. So I became wealthy and in 2004, I sold a zingy for $80 million and I own 53% of the company. So I made $43 million net of tax. It was like 26.5. And what’s interesting is in a way it didn’t change anything.
I still lived in a studio apartment for a few more years. I think the big purchase of that time, it was the next box of TV and two tennis rackets mostly driven by how busy I was. Like we were growing, we grew from 15 million in revenue. So for it’s two hundred and two oh five. I can moving offices every four months and thinking we re-did that.
And like it kept, we kept getting bigger and bigger offices and hiring. So it didn’t really hit me completely. What’s interesting is my first company where I built in 98, 99, like my company on paper is worth hundreds of millions and that it comes so easily that I didn’t realize how much money that was like at 28.
I started my bath company at 23 is like an eBay of Europe. We had a buyout offer. 300 million at 40% a company, I was going to make $120 million. And again I’m like, man, of course everyone makes money to me. Other than that, it’s just a bubble. Everything seemed easy. I did not realize how, because you, 23, you don’t know any better.
And also I never really lacked for money. And also I never really, I never money was never an objective. It’s like a means. It’s not even a Misa net. I want to be a tech founder. That’s all I wanted to be. And whether or not I was going to be financially successful was irrelevant, which is why, by the way, in 2006, After the bubble bursts and, I made I went from hero to zero basically, and was bankrupt in 2001.
Then I realized maybe I should have taken a secondary for a couple of million, which is people will offer it. And I’d be like, nah, a couple billion who need, I want to be Bebe. The founder of there’s all in. I don’t want to take money off the table, et cetera. I’d like a more to prove I want to be the ideal entrepreneur.
And of course for me, I thought like a couple of millions, nothing. It forced at that point, I was thinking that having literally nothing in my bank account that I realized, oh shit, no money is really hard to make. It’s very easy to lose. It’s very hard to make. But in 2001, when I would have built zingy.
This internet thing is it’s dead. It’s small. It’s not big and no big deal. At the end of the day, I didn’t do this for the money. I did this to be, I wanted to create something and nothing. I’d love tech. So I’m going to build a new company. It’s probably not going to be big and it doesn’t matter. Now, lo and behold, it turns out I made sure that it wasn’t dead.
Despite every company had got on web van Petlock com MCI work on everyone had got under. And at that point in time and VC soft investing, but came back and B was financially successful. Now what has done for me since is I value experiences and I value my time. And so what I use the money for is I have a, I have a Butler or a an estate manager and who’s also my chef and does all of the offline things that I don’t like to do, so I don’t cook. I don’t clean. I et cetera. I have a virtual assistant in the Philippines and managers of my entire life. I. I go heli skiing, which is extraordinary, expensive, by the way for fun. Now I don’t own any physical goods per CyberKnife. I have a house in Turks. I have a house and I have a department, New York avenue.
I have a house in Revelstoke, but I don’t have, yeah. I really have a sense of cars or clothing and luxury, et cetera, all those things. I don’t think mattered too much for me. I think physical goods are anchors. But for me it’s more using the financial success I’ve had as a means of buying Experiences.
I love helping people around me and I give millions a year, but beyond giving millions a year to charity, I actually give millions a year to my friends as a means of changing their lives and making the, making a difference on the day to day of their life. And it’s a bit non-traditional other way.
But these are people I’ve known for 20, 30 years. And so I tell them, don’t expect it to be recurring. It just happens when I have an exited where I feel you’re in need and it’s meaningful for them. And I don’t think it impacts our relationship. So I think it’s been an amazing tool and it’s also been amazing to have freedom.
Like my dream, for instance, in and FJ labs is actually not to have external investors. If it’s the maximum I can invest with my current strategy is 300 million a year. If I have 300 million a year of I owed money to deploy, I would do that and not have any external capital. That would be way easier. That would remove the part of my life that I don’t like of dealing with LPs and fundraising and like and whatever, a gap, accounting and sec registration and all that stuff.
I would do that in a heartbeat. Financial success is really a means of free personal freedom to do what you want. When you want to have the experiences you want to have and to help the people around you.
MPD: Was there a moment when you felt like you got your sea legs with being wealthy, where it went from, figuring out what that meant for you to, okay.
I got it. I know my framework for how I want to use money to have impact my friends, my personal life, et cetera.
Fabrice Grinda: Eh, happened automatic over time automatically like the. I soon as I add capital, I started investing in startups. So I really stayed all by angel investing in 2005 and I knew I wanted to deploy capital into.
To back the, my friends were building companies and to help them realize their dreams and to solve the problems in the world. So that immediately came to me in terms of helping my friends did that leader, but I realized how, what I started considering like a little capital could change.
It could make a difference in the lives of my friends, a friend of mine, she was running a dermatology clinic in New York and she was making whatever a half a million a year. And she decided to said to go run a cancer research, live at Harvard and make like whatever, a hundred K a year. Profound difference in her income yet for the world.
I thought I was like a massive net positive contribution, but as a result, she could no longer afford like the down payment or a house in Boston. So I paid that for her and I think it’s the right thing for you and your husband and your kids to be able to love and amazing place. So you can actually do research this meeting folder of the world and that sort of happened.
Little by little over time. No, I’m not sure there was ever like a, oh, this is a correct strategy. Very rapidly. What I did realize is I don’t, I never followed traditional wealth management advice. You go to these wealth managers or like Goldman or whatever, and they’re like, oh, you should have 50, 60% equities and 30% bonds and blah, blah, blah, like crazy.
None of that ever made any sense to me, I have a complete barbell portfolio where it’s like a 10% of cash because you want optionality of being able to take advantage of things in crises, 10%, crypto, 10% public Sox of the things that have gone public in my portfolio that I still like and old 10% of real estate that’s really consumption.
And then everything else is like early stage Texas tech stuff. A completely barbell works really well. I realized it was much better at doing that. And ma which is essentially the same thing as like running FJ labs. If your labs are in a ways, a family office, and good on that front. And I made many mistakes.
Like I, I lost in a way millions dollars and Billy’s trying to buy a big chunk of the country to preserve the rainforest, which, taught me something about a rule of law. I lost millions dollars in Dominican Republic doing something at a much smaller scale, instead of hundreds of thousands of acres doing it with 165 acres, wanting to build a big community where I would bring founders and spiritual leaders and and artists to just create and be there with no business model, but like everyone from the mayor to the minister of tourism and environment, all wanted bribes and create an environment that was all super tenable.
So lost millions of dollars. Pursuing, if you, these houses, I made many mistakes along the way, but in general, at the end of the day, my true north star of help those around you. Help the world through, in my case, second Vaseline. So like finding solutions, the world’s problems, and like by yourself and living the life you want to lead has been amazing.
By the way, through that process, I did a lot of iteration in 2013. I’d actually 2012. I gave almost all my physical possessions to charity. I went down to 50 items that fit in a carry on my backpack and my tennis bag. And I went cap surfing and France couches for a year that I went like an Airbnb.
I lived in Airbnbs and hotels for three years beyond that all around the world. Like making sure I allocate time to invest in my friends and friendship and my friendships and my family in a way I’d never done that before.
MPD: And why did you need to do that? Just cause the material items were owning you at some level.
Was that the thinking, did you have all the goods to do that? To have related
Fabrice Grinda: time allocation? If you have like at a country house in Bedford and I would go and it was amazing, right? Like I, it was huge and we played paintball there and like it organized like parties. We played video games the way they gave me a room, et cetera.
But at the end of the day I went there because I was paying so much for it, which is the wrong reason to use something. The minute I didn’t have an apartment, the minute I didn’t have a house, I was like, okay, dad, I have infinite freedom and flexibility. Where do I want to be? Who is it that I want to be spending time with?
And so being, when you have a default, you go to that default, if you remove the default option, you can be way more thoughtful about what it is you really want to do, who it is, what it is you really want to hang out with. And the fundamental problem I was trying to solve for is. As you get older as your friends.
And I start getting married, having kids jobs, et cetera. I like the quality of the tea. The texture of your friendships, like changes when you’re in college, you’re remaking the world. You’re starting to you’re seeing your friends seven days a week. Even at McKinsey, I would see my friends date many days.
Many hours every week. And all of a sudden it would came at like the biographical update. I, we see you once every six weeks. And at that point is what happened to your husband and your work, et cetera, and your kids since then? And it’s fine, but it’s not the reason that we became friends. We became friends because there was a more fundamental connection and perspective and beliefs of some of the world and extraordinary conversations.
And I wanted to rekindle that in, in my thirties, in a eighties, it seemed to have gone away between the age of 25 and whatever 35. And I’m like, there must be a way to change it. And others were not making the adjustments to their little. Why don’t I adjust my life to make it happen. And now there are many false starts, right?
Like the couch surfing was a total failure because of course it was Dean and cab. The fact that I was at a position in their life and they saw, I’d like to bring skids to school and go to work, et cetera. The Airbnb thing worked really well until her BB was made illegal. It may most of the major cities and like across New York, all the high-end inventory to spirit then they will tell us all became full.
So I was like moving hotels every four days. So that’s actually the reason I ended up buying an apartment in New York. I was very happy living in like billionaires apartments, for a month, at a time in every neighborhood in New York, hosting dinner parties there. But once I had to live at hotels and move a tell, remember five days, I’m like, okay, that’s not viable.
And I couldn’t find high-end re rental inventory. I liked, so I bought a place, but. I guess people don’t put enough iteration and design and thought into their lives. They follow the default, whereas you can throw stuff on the wall and see what sex and see what sticks for you, right? Like people are built differently and what they want to do and how they want to lead their lives.
And they followed the, I guess thing, the default path way too much. Like my life is very non-traditional in general. I do a month in New York than a month intrusive kaikos I’ll do a month in Canada. Because New York and is socially artistically, professionally extraordinary intense.
And if you’re doing, you’re not thinking, and then I come to church and I’m working during the day. I’m in trucks right now and we’re doing this call and I have 12 calls today, but I’ll meditate. I’ll go, kitesurf, I’ll play tennis. And I’ll take the time to read and write and think and be reflective and rebuild my batteries.
And then most people don’t necessarily think through what is right for them in light of their energy level, personality, et cetera. And so that iterative design is alive, made it alive by.
MPD: I love all that. You mentioned through there that you do a lot of charity, which I think is great. I particularly was interested in the buying a Britain forest or attempts to do taking it that further.
I would love to hear your take on impact, right? Is there a cause that you’re passionate about or some particular topic? Let me put it a different way, because my favorite way to ask this question, if you were king now, president king, what is one thing you would change?
Fabrice Grinda: So I’m going to give the hyper rational answer to that.
Please, if you look at all the policies you could do in the U S and which ones would actually impact wellbeing for people the most it’s actually, there’s one thing that has much larger impact on personal outcome than everything else. And in the U S social mobility as a client, it used to be the 95% of people made more money than their parents.
Now it’s about 50% since people born since 1982. And the main reason for that is that the top cities are the ones where all the jobs created for all the opportunities are, have become unaffordable. And the reason there aren’t affordable is we’ve passed extraordinarily idiotic, zoning and landscaping laws.
And at that, that mean that you cannot build as easily as you should be able to. And there’s a lot of reasons for that. If your current owner restricting supply means your thing your homes increasing value dramatically. But it’s extremely bad for like social mobility economic diversity.
And so you look at San Francisco, 80% of the city is zoned. Apartments are illegal. You can not have more than two story buildings. And as a result, you have the cities become extremely unaffordable. So if I could change one, one thing is essentially. Remove all air rights, all essentially zoning and construction regulation.
Other than a few, see if you’re not going to be building over whatever central park, but like air rights and city and your city make no sense. Like having these buildings that are less than a hundred year olds old, be like landmark that you can’t build over them makes no sense. You should be able to build up as much as you can.
And we should have unlimited supply. And of course, there’ll be a lag of eight years or 10 years before things get built and prices adjust. But at that actually solves affordable housing. And when you solve affordable housing, you recreate mobility and your lack of people to get the best jobs. And this is what changes the outcome more than anything else.
Now that’s not a something I’m investing in any way, shape or form or. Because there’s crazy nimbyism and political forces against it. And it’s, it has to be in the U S the rules are like literally like neighborhood by neighborhood. And it’s so painful. So I, as king, I would do that. That is not where I keep my claim to.
Now I’ve not put a lot of thought into charity. That first of all, what I do at the charity level, it is way more personal and directed will have a much larger impact on the lives of the people I help, but it’s much more smaller scale. Like in the Dominican Republic, I helps pay for the education of 10,000 kids from K through 12.
It’s amazing for these kids. So it changes their life outcomes, dramatically program.
MPD: You do that through, or you just set that up.
Fabrice Grinda: No, it’s the dream project that I was funding. And I, but I helped them beyond that. I helped, I built like a tech center where they could learn programming and to have access to computers and internet and find jobs, et cetera.
I fund something called the university of the people, which is helping non low-income people basically get us degrees, especially in things like computer science. And there are people from like our over a hundred nations and they often end up getting jobs at Google, Facebook, et cetera.
So it’s been mostly right education, helping people be able to increase their out their life outcomes through adhesion often in the communities where I was living, I lived in the Dr for largest spend, like four or five months a year from 2012 to 2019 2018, the men I’ve done a lot of that now, separately I’ve dragged given directly.
Contributions to many of my friends and like dozens of them, right? And we’re talking millions and millions of dollars, it’s life-changing for them, but I don’t larger scale. All of that is dwarfed from a social and economic impact by what I do. And as a tech investor, right? Like my tech investments of hundreds and hundreds of companies, I think ultimately will change the lives of billions of people.
And yeah, they’re for profit, but there’s a fundamental social motivation for them. And I think they will dwarf anything I do on the direct investment and the direct shadow charity frame. That’s why most of my personal capital is actually allocated to investing technology, to solve the world’s problems.
And I think we will, by the way, I’m extremely optimistic on how we’re gonna address climate change, inequality of opportunity, et cetera.
MPD: It’s been great having you on. Thank you so much for doing this.
Fabrice Grinda: Thank you for having me
MPD: every time I talked to Fabrice, I feel a little bit smarter, very grateful for him being on the show today and grateful to have him in my orbit, working together and doing deals together. It’s a great guy. If you liked what you heard, please hook us up with a like or a five-star review. This is my basic pandering.
Help us out. You can find me on Twitter at MPD. And to hear more of my conversations with innovators, subscribe on YouTube, Facebook, or any major podcast platform. Just search for innovation with Mark Peter Davis.